iSCSI, or Internet SCSI, is a standard developed by the IETF for mapping SCSI data blocks into Ethernet data packets. Fundamentally speaking, it is a new type of storage technology based on the IP Storage theory. It combines the SCSI interface technology widely used in the storage industry with IP network technology to build a SAN on an IP network. Simply put, iSCSI is a network storage technology that runs the SCSI protocol on an IP network. iSCSI technology was originally developed by both Cisco and IBM, and has received strong support from IP storage technology enthusiasts. It has grown rapidly in recent years.
iSCSI is a good choice for SMBs' storage networks. First of all, in terms of technology implementation, iSCSI is a technical standard based on the IP protocol. It allows the network to transmit SCSI commands over the TCP/IP protocol to implement SCSI and TCP/IP protocol connections so that users can access the TCP/IP network. Building a SAN requires only a small amount of investment, so that information and data can be interactively transmitted and managed easily and quickly. However, before the advent of iSCSI, the only technology for building a SAN was to use Fibre Channel, which required a large amount of construction costs, and SMEs generally could not afford it. Secondly, iSCSI technology solves many problems in terms of transmission efficiency, storage capacity, compatibility, openness, and security. In terms of performance, it is absolutely not lost to commercial storage systems or fiber storage networks.
The advantages of iSCSI mainly include: First, iSCSI follows the TCP/IP protocol, while TCP/IP is the most common and mature protocol in the network, and the infrastructure of the IP network is perfect. At the same time, SCSI technology is used by disks and tapes. Storage standards widely used by other devices, these two points make iSCSI construction costs and maintenance costs are very low; Second, iSCSI supports general Ethernet switches rather than special Fibre Channel switches, thereby reducing the trouble caused by heterogeneous networks; Also, iSCSI transmits storage commands via IP packets, so it can transfer data across the Internet without distance limitations.
FC SAN and IP SANAfter the advent of iSCSI technology, storage networks built using IP technology have also emerged. There are two different implementations of SAN technology, FC SAN and IP SAN. In simple terms, a storage network built with fiber is an FC SAN. Storage networks built with iSCSI technology are called IP SANs.
As two implementations of the SAN, the FC SAN and the IP SAN have advantages and disadvantages. The following describes each of them in several aspects.
In terms of data transmission, both FC SAN and IP SAN are implemented using block protocols. This is their common point.
In terms of transmission speed, FC SAN (2Gbit/s) is the fastest and iSCSI (lGbit/s) is the nextest.
In terms of transmission distance, the FC SAN can theoretically reach 100 kilometers. In fact, after more than 50 kilometers of transmission, there will be a bottleneck. There is no theoretical distance limit for iSCSI technology over IP networks, i.e., iSCSI can perform data transmission without distance restrictions.
In terms of management and maintenance costs, setting up an FC SAN network requires a lot of hardware costs, and requires specific tool software for operation and management, while IP SAN construction costs low. Because iSCSI transfers data and allocates storage resources over an IP network, Manage and use the existing network, so you can save a lot of management costs and training costs.
In fact, IP SAN also faces some unavoidable problems: First, IP SAN-based network storage has not yet been fully recognized by users. Second, IP SAN storage requires specialized drivers and equipment. Fortunately, some traditional fiber adapter vendors All released iSCSI HBA devices, while Inter also introduced a dedicated IP storage adapter, and Microsoft, HP, Novell, SUN, AIX, Linux also has iSCSI IniTIator software, and free for users to make
With: Also, in terms of security, although the IP SAN has a set of standardized security mechanisms, it has not yet been approved by users.
Although these problems and troubles will hinder the development of iSCSI, it is believed that in the future of the network storage world, IP SAN absolute gold has a place.
The composition of iSCSIA simple iSCSI system consists roughly of the following parts:
iSCSI IniTIator or iSCSI HBA iSCSI Target Ethernet Switch One or more servers
The topology of a complete iSCSI system is shown in Figure 7-1.
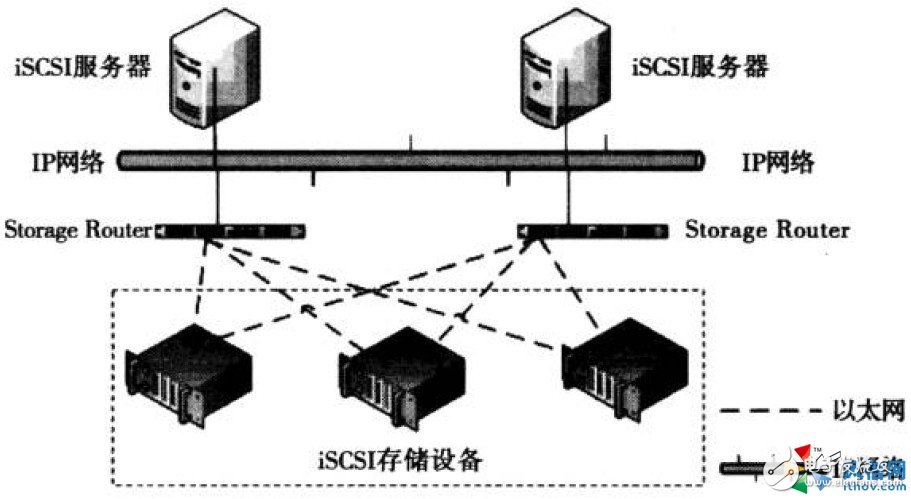
In Figure 7-1, the iSCSI server is used to install the iSCSI driver, iSCSI IniTIator. The Storage Router can be an Ethernet switch or router. The iSCSI storage device can be an iSCSI disk array or a PC server with storage function. The following describes in detail the meaning of the iSCSI IniTIator and iSCSI Target.
iSCSI InitiatoriSCSI Initiator is a software or hardware device installed on a computer that is responsible for communicating with iSCSI storage devices.
There are two ways to connect an iSCSI server to an iSCSI storage device:
The first is a software-based approach, iSCSI Initiator software. After the Initiator is installed on the iSCSI server, the Initiator software can virtualize the Ethernet card as an iSCSI card, and then receive and send iSCSI data packets to implement the iSCSI protocol and TCP/IP protocol transmission between the host and the iSCSI storage device. This method requires only Ethernet cards and Ethernet switches, no other equipment, so the cost is the lowest. However, the conversion of iSCSI packets and TCP/IP packets consumes a part of the CPU resources of the iSCSI server. This method can only be used in applications with low I/O and low bandwidth performance requirements.
The second is the hardware iSCSI HBA (Host Bus Adapter) card mode, iSCSI Initiator hardware. This method requires the purchase of an iSCSI HBA card and then installing it on an iSCSI server to achieve efficient data transmission between the iSCSI server and the switch and between the iSCSI server and the storage device. Compared with the first method, the hardware iSCSI HBA card method does not need to consume the iSCSI server CPU resources, and the hardware device is dedicated, so the hardware-based iSCSI Initiator can provide better data transmission and storage performance. However, iSCSI HBA cards are relatively expensive, so users have to weigh their performance and costs.
iSCSI Initiator software is generally free. Centos and RHEL have very good iSCSI Initiator support. The current Linux distributions come with the iSCSI Initiator by default.
2, iSCSI TargetAn iSCSI disk array or iSCSI capable device that can be used to store data can be referred to as an "iSCSI Target" because most operating systems can use some software to turn the system into an "iSCSI Target." This chapter focuses on how to build a PC-based iSCSI storage system. The so-called PC architecture is to select an ordinary, high-performance PC that can support multiple disks (usually a PC server), and then select a relatively mature and stable iSCSI Target software, and install the iSCSI Target software on the PC server. The ordinary PC server is transformed into an iSCSI storage device and provides iSCSI data transmission services through the PC server's Ethernet card.
At present, most iSCSI Target software is charged, such as DataCorc Software's SANmelody, FalconStor Software's iSCSI Server for Windows, etc. These are supported on the Windows platform. However, there are also open source iSCSI Target software for Linux platforms, such as the iSCSI Enterprise Target, which will be highlighted later.
With iSCSI Target software, the storage space of the server can be allocated to the client. The client can use the iSCSI disk like a local hard disk, including partitioning, formatting, and reading and writing. And each client can write data to the iSCSI disk without disturbing each other and it will not destroy the data stored in the server. At the same time, iSCSITarget software has very flexible user rights control and supports configuration files.
We know that iSCSI communicates using the TCP/IP protocol. Therefore, connecting both ends of iSCSI requires only one Ethernet network. It can be seen that the storage performance of iSCSI is directly related to this Ethernet network. Therefore, it is best to use Gigabit Ethernet switches in iSCSI networks. Inferior network devices will seriously affect the performance of the storage system. That is, for each The server is equipped with high quality Gigabit Ethernet switches and provides two connections. For iSCSI Target, two independent ports in each independent array should be equipped with switches. Finally, the switches are connected. In this configuration, even if one of the two switches fails, the entire iSCSI storage system can still work properly. This ensures the uninterrupted operation of the storage system.
How does iSCSI work?To understand the working principle of iSCSI, you must know the iSCSI hierarchy. According to the OSI model, the iSCSI protocol can be divided into three layers from the top to the bottom, as shown in Figure 7-2.
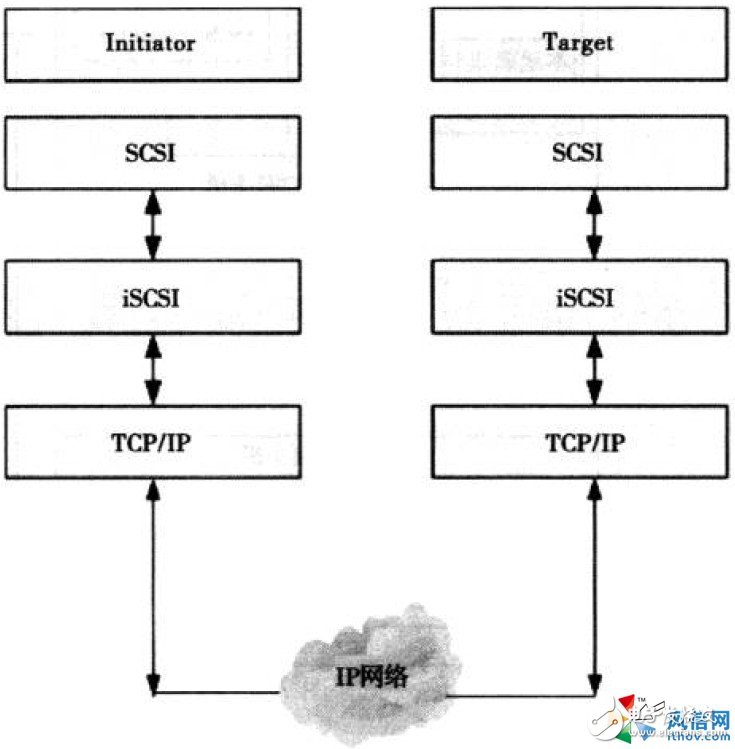
Each layer is briefly described below.
SCSI layer: SCSI CDB (command description block) is established according to the request sent by the client and passed to the iSCSI layer. Receives CDBs from the iSCSI layer at the same time and returns data to the application.
iSCSI layer: The SCSI CDB is encapsulated so that it can be transmitted over the TCP/IP protocol-based network to complete the SCSI to TCP/IP protocol mapping. This layer is the core layer of the iSCSI protocol. This chapter also focuses on the configuration and management of this layer.
TCP/IP layer: It routes and forwards IP packets and provides transparent and reliable end-to-end transmission.
The iSCSI protocol defines the rules and methods for sending and receiving data blocks in a TCP/IP network. The sender first encapsulates the SCSI commands and data into TCP/IP packets, and then forwards them over the IP network. After the receiver receives the TCP/IP packets, it restores them to SCSI commands and data and executes them. After the execution is completed, they will be returned. SCSI commands and data are re-encapsulated into TCP/IP packets and then sent back to the sender. This completes the entire process of data transmission.
The entire data transfer process of iSCSI is totally transparent to the user. The user uses the remote storage device just like the local hard disk device. However, this is only a theoretical state. In fact, the data transfer rate of iSCSI does not completely reach the data transfer rate of the local hard disk, but the difference is not obvious. Moreover, this network storage model has the advantage of high security, which is obviously very important for iSCSI stored in the data set.
Puff Series,Puffs Vape,Puff Flex,Puff Flex Vape
Shenzhen Zpal Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zpal-vape.com