Pulling current and sinking current are the parameters that measure the output drive capability of the circuit (note: pull and fill are both on the output side, so it is the drive capability). This is commonly used in digital circuits.
The first thing to note here is that the pull-and-sink current in the chip manual is a parameter value, which is the upper limit (allowed maximum value) that the chip allows the output to pull and sink in the actual circuit.
The concept to be discussed below is the actual value in the circuit.
Since the output of the digital circuit is only high and low (0, 1), the high level output is generally the output terminal provides current to the load, the value of the current supply is called "pull current"; low level output When the output current is generally absorbed by the load, the value of the absorbed current is called the "injection current."
For input current devices:
Both sinking current and sinking current are input,
Injecting current is passive,
Suction current is active.
If the external current through the chip pin into the chip 'inflow' is called the sink current (is poured);
Conversely, if the internal current is 'flowed' from the chip through the chip pin, it is called pull current (pulled out).
2. Why can we measure the output drive capability?
When the logic gate output is low, the current gated into the logic gate is referred to as sink current. The higher the sink current is, the higher the output level is. The triode output characteristic curve can also be seen that the larger the sink current, the greater the saturation voltage drop and the higher the low level.
However, there is a limit to the logic gate's low level, which has a maximum UOLMAX. It is not allowed to exceed this value when working on logic gates. The specification for TTL logic gates specifies UOLMAX ≤ 0.4 to 0.5V. Therefore, there is a ceiling on current sinking.
When the logic gate output is high, the current at the logic gate output is flowing from the logic gate. This current is called the pull current. The larger the pull current, the lower the output high level. This is because the output stage transistor has internal resistance, and the voltage drop on the internal resistance causes the output voltage to drop. The larger the pull current, the lower the output high level.
However, there is a limit to the logic gate high, which has a minimum value of UOHMIN. It is not allowed to exceed this value when working on logic gates. The specification of TTL logic gates specifies UOHMIN ≥ 2.4V. Therefore, there is also an upper limit on the pull current.
It can be seen that both the output current and the sink current have an upper limit. Otherwise, when the output is high, the output current will be lower than UOHMIN. When the output is low, the output current will be higher than UOLMAX. Therefore, the pull current and sink current reflect the output drive capability. (The larger the value of the pull-and-sink current parameter of the chip, the more the chip can receive more load because, for example, the current is supplied by the load. The more the load, the greater the current to be injected).
Since the high-level input current is very small, it is generally unnecessary to consider in the micro-ampere range, and the low-level current is larger at the milliampere level. Therefore, there is usually no problem if the low-level current is not exceeded. The fanout coefficient is used to describe the ability of the logic gate to drive the same type of door. Fanout factor No is the ratio of the low-level maximum output current to the low-level maximum input current.
In integrated circuits, current sinking, current sinking, and current sinking are important concepts.
The pull is discharged and the active output current is output from the output port.
Irrigation charge, passive input current, is flowing from the output port
Suction is active suction current that flows in from the input port
Suction and sinking currents are the currents flowing from the external circuit to the chip through the pins. The difference is that the sink current is active. The current flowing in from the input terminal of the chip is called the sink current. The current injected is passive, and the current flowing from the output is called sink current.
Pulling current is the output current provided by the digital circuit output high level to the load. When the current is sourcing, the output low level is the external input current to the digital circuit. They are actually input and output current capabilities.
The sink current is for the input terminal (input terminal sink); the pull-out current (output terminal) and the sink current (output terminal for sink) are relative to the output terminal.
Give an intuitive explanation:
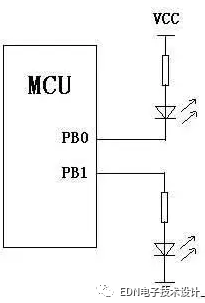
PB0 output 0 in the picture, the LED will light, the current direction of PB0 is flowing to PB0, that is to sink the current; And PB1 wants to output 1, LED will light, the direction of PB1 current flows from PB1, namely pulls the electric current.
In the actual circuit, the current is formed by the input of the low-level current input by the subsequent logic gates, which is formed by filling the output of the front logic gate. The reader refers to Figure 18-2-3. Obviously, its test circuit should be as shown in Figure 18-2-4(b). The logic level applied to the input terminal is to ensure that the output terminal can obtain a low level, but the current is supplied to a potential connected to the power supply. Obtained by the device, adjust the potentiometer can change the size of the current sink, the output voltage of the low level will also change.
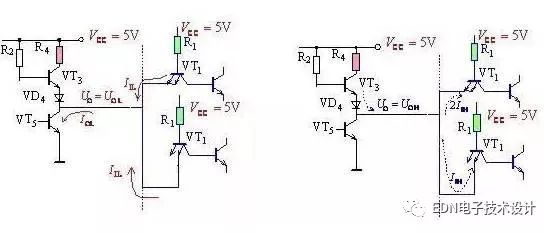
(a) Sink current load (b) Pull current load
Figure 18-2-3 Sink current and discharge current
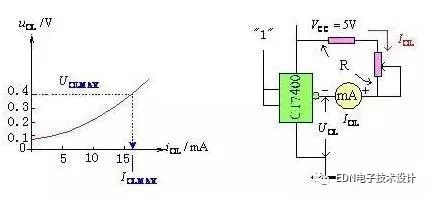
(a) Sink current load characteristic curve (b) Test circuit
Figure 18-2-4 Sink current load characteristic curve and test circuit
When the output low-level voltage value increases to the output low level maximum as the sourcing current increases, that is, the corresponding sourcing current value when uOL=UOLMAX is defined as the large output value IOLMAX of the low-level current.
Different series of logic circuits, different types of integrated circuits in the same series, the national standard in the specification of the maximum value of the output low-level current IOLMAX specifications are often different. The more commonly used values ​​are as follows
TTL Series IOLMAX=16mA
LSTTL74 Series IOLMAX=8mA
LSTTL54 Series IOLMAX=4mA
The Fanout Factor, NO, is a parameter that describes the load capacity of an integrated circuit. Its definition is shown in the following 18-2-1.
NO= IOLMAX / IILMAX
Where IOLMAX is the maximum allowable sink current, IILMAX is the current that a load gate sinks into this stage.
The larger No is, the stronger the load capacity of the door is. General product regulations require No ≥8.
When determining the fan-out coefficient, it is important to calculate the current value correctly. For Figure 18-2-3, the input of the logic gate that follows is connected in parallel. When the output is low, the IIL flowing from the input of the logic gate behind has no effect because of the current limiting effect of R1. However, when the output is high, the direction of the current changes to flow into the input, and the multi-emitter transistor of the logic-level input stage has two parallel transistors. The incoming IIH will have to double, related to the number of parallel terminals. For Figure 18-2-3, where NOL = 2, and NOH = 3, both the output low level and the output high level, the fan-out coefficients may be different. Since the value of IIL is much larger than the value of IIH, the main aspect of the conflict for integrated circuits is the low-level fanout coefficient. Therefore, generally, we only need to consider the low-level fan-out factor.
Which is the most welcome kid laptop for entertainment and online learning? 10.1 inch laptop is the best choice. You can see netbook 10.1 inch with android os, 10.1 inch windows laptop, mini laptop 10.1 inch 2 in 1 windows, 10.1 inch 2 In 1 Laptop with android os. Of course, there are various matches of memory and storage, 2 32GB or 4 64GB. Our suggestion is that 10.1 inch android 32GB laptop, 10.1inch 32GB or 64GB Solid State Drive windows laptop. Except 10.1 inch Student Laptop , there are 11 Inch Laptop, 15.6 Inch Laptop, 14 Inch Laptop , also option here.
Besides, other advantages you can see on 10.1inch Budget Laptop For Students, for example, lightweight, competitive cost, portability, Android or Windows OS, rich slots, energy saving cpu, etc.
As a professional manufacturer, can provide free custom service, like mark client`s logo on laptop cover, opening system, inner color box, manual, boot. Produce as your special requirement on parameters, preinstall apps needed, etc. What you need to do is very simple, confirming PI, including price, delivery time, parameters, etc.
10.1 Inch Laptop,Netbook 10.1 Inch,10.1 Inch 2 In 1 Laptop,10.1 Inch Windows Laptop,Mini Laptop 10.1 Inch
Henan Shuyi Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.shuyicustomlaptop.com