With the rapid development of computer and communication technologies, the global information network is rapidly evolving to the IP-based Next Generation Network (NGN). In the future, the trend of broadband and mobile technology for personal multimedia communications in the world, coupled with market demands for flexibility and convenience, make the goal of seamless coverage and wireless connectivity increasingly becoming a reality. At present, various wireless technologies present a situation of blooming and arguing, which accelerates the popularity of wireless applications and faces problems that cannot be ignored due to the inherent frequency interference of wireless technologies.
1. Analysis of frequency interference principle of wireless communication systemThe generation of wireless interference is various. The original dedicated radio system occupies existing frequency resources, improper network configuration of different operators, transmitter self-setting problems, cell overlap, environment, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), etc. The cause of radio frequency interference in wireless communication networks. Coexistence interference between systems operating at different frequencies is essentially due to the imperfections of the transmitter and receiver. In general, active devices emit unwanted signals, and due to the limitations of the device itself and the out-of-band rejection of the filter, unwanted signals such as spurious, harmonic, and intermodulation are generated outside of its operating band. It interferes with the operating band of other wireless systems.
For wireless systems, the transmitter generates out-of-band radiation when it transmits a useful signal, including adjacent-frequency radiation and out-of-band spurious emissions due to modulation. While receiving the wanted signal, the receiver may fall into the interference signal of the channel, which may cause loss of receiver sensitivity. Interference signals falling within the receiving bandwidth may cause in-band blocking. At the same time, the receiver also has nonlinearity. Imperfect, out-of-band signals (transmitted useful signals) can cause out-of-band blocking of the receiver.
In addition to the quality of the device itself, the intensity of unwanted signals generated by active devices, such as out-of-band spurs, harmonics, and intermodulation, is related to two factors: the greater the output power of itself, the greater the output of unwanted signals; The extent of deviation from the working bandwidth, the farther away from the working bandwidth, the smaller the unwanted signal. The tolerance of the system to external interference is also related to two factors: the strength of the signal itself, the stronger the signal, the less the chance of interference; the smaller the interference signal, the smaller the interference signal level, and the lower the signal interference. In addition, the interference between the transmitter and the receiver is also dependent on factors such as the separation of the operating bands of the two systems and the spatial isolation of the transceiver.
The interferences of wireless and mobile communication systems mainly include co-channel interference, adjacent-frequency interference, out-of-band interference, intermodulation interference and blocking interference.
2. Frequency interference of wireless communication systemsFrom the actual situation in China, the main wireless communication technologies will be: GSM and narrowband CDMA belonging to the second generation of cellular mobile communication technology, PHS (Little Smart) and SCDMA (Greatly Linked), which are fixed by fixed telephones, and belong to the third TDD system for cellular mobile communication system TD-SCDMA and FDD system WCDMA/DMA2000, WLAN/WiMAX for broadband wireless access, UWB for short-range communication, and FRID for wireless identification. Although the application areas of these technologies overlap, their specific market needs will coexist for a long period of time, so their interference must be considered.
2.1 Existing wireless communication spectrum solutions
The specific allocation of the existing wireless and mobile communication spectrum in China is shown in Figure 1. In addition, the WLAN uses the unlicensed ISM band, UWB uses the 3.5/5.8G band, and WiMAX and RFID have not yet finalized the band, of which WiMAX may be allocated. In the 2.5G, 3.5G or 5.8G frequency band.
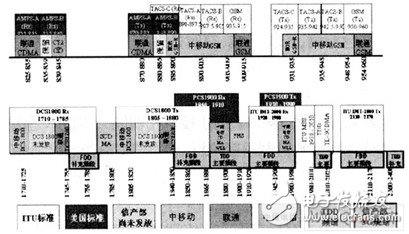
Figure 1 Existing spectrum allocation for wireless communication technology in China
2.2 Basic situation of wireless interference
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the frequency bands of GSM1800, PHS, SCDMA, TD-SCDMA, CDMA2000, WCDMA and other wireless systems are directly adjacent or coincident, which is difficult to avoid mutual interference, and UWB's ultra-wideband characteristics will also cause interference. ,as shown in picture 2.
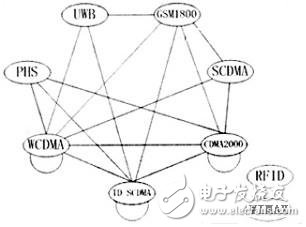
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of wireless interference
2.3 Mobile communication system interference
The various interferences in a mobile communication system can be generally classified into interference within a cell, interference between cells, interference between different communication systems, interference between different operators, interference caused by system equipment, and the like.
Interference in the small area mainly includes multipath interference, near-far effect and multiple access interference. The generation of these interferences is determined by the time-varying of the wireless channel and the delay and fading during the propagation of the electromagnetic wave. The interference generated when the adjacent cells use the same frequency is especially serious for the TDD system. The interference between the TDD system and the FDD system is mainly the interference between the TDD channel (including the uplink channel and the downlink channel) and the FDD uplink channel. In addition to the above interference, interference between different operators, interference caused by system equipment, etc. are also issues that need to be considered.
3. Interference solutionAlthough the interference in the wireless communication system is ubiquitous, according to the analysis of the root cause and interference situation of the interference, combined with computer simulation and a wide range of field tests, some effective methods for reducing and eliminating interference are also found. These methods are mainly divided into two categories: basic technology and engineering construction.
86x86mm low Profile White Faceplate
Ideal for Solid Cat 5 or Cat 6 cable
This faceplate could be include or exclude the Keystone Jack
Provided with fixtures and fittings
could be supply 1 port, 2 ports, 3 ports, 4 ports, 6 ports, 8 ports for your choice
White is the common color, we also supply the ivory, black, and other colors customized
86 Type Face Plate,Brush Wall Faceplates,Wall Face plates
NINGBO UONICORE ELECTRONICS CO., LTD , https://www.uniconmelectronics.com