According to the “Internet of Things†report proposed by the International Telecommunication Union, there are four key application technologies for the development of Internet of Things technology, RFID, wireless sensor network WSN, intelligent technology and nanotechnology. Among them, RFID and WSN are in the forefront of four key application technologies. RFID and WSN have different origins, development and application priorities. However, with the continuous development of both technologies, the integration of RFID and WSN has become a trend. RFID was born earlier, initially to facilitate identification of the item number information, its tag structure is also very simple, only store simple ID information, activated by the reader through the radio. As technology continues to advance, the functionality of RFID tags is becoming more sophisticated, and microprocessors, batteries, and communication transport protocols are being added. This transition is increasingly close to the nodes in the WSN, if the RFID system is associated with the WSN. The combination will make the collection of tag information more convenient and intelligent, and the powerful network function of WSN can expand the transmission range of RFID system identification information; from the perspective of wireless sensor network, its research content focuses on network connection. The collection of sensor information and the addition of RFID technology have enabled sensor network applications to find new breakthroughs. Therefore, RFID systems and sensor network technologies have certain complementarities, and their combination is of great significance.
1 Radio frequency identificationRadio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon (RFID), as the basis for high-tech and information standardization for fast, real-time and accurate information collection and processing, has been recognized by the world as one of the ten most important technologies of this century. In recent years, with the development of technologies such as large-scale integrated circuits, network communication, and information security, RFID technology has shown great development potential and application space. Due to its high-speed moving object recognition, multi-target recognition and non-contact identification, RFID Major projects in the fields of logistics, transportation, telecommunications, agriculture, animal husbandry, civil aviation, bills, anti-counterfeiting, safety and medical care have been piloted and applied, and achieved good results. Compared with other identification technologies, RFID works without manual intervention, can automatically work in a variety of harsh environments, can read and write tags, data encryption and many other advantages, improve people's quality of life, improve business efficiency, and strengthen public safety. Production is of great significance. As technology matures and costs are further reduced, RFID is gradually being applied to all walks of life, especially in the areas of government-administered public utility management, such as financial IC cards, traffic cards and mobile payments. A typical RFID system is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Block diagram of the RFID system
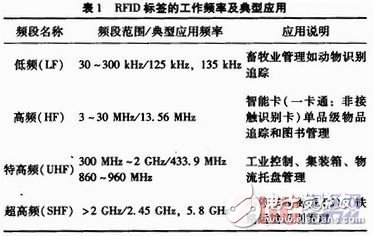
A typical RFID system generally consists of a reader, an electronic tag, an RFID middleware, and an application software system. The reader establishes two-way communication with the tag, usually consisting of a radio frequency interface, a logic control unit and an antenna 3; the tag is used to store the identity and attribute information of the identified item, and belongs to the identification device of the identified item, usually attached to the surface of the identified item. Or internal, is the electronic data carrier of the RFID system, which is composed of an MCU, a coupling coil, a rectifying and filtering circuit and an autotransformer; the reader can notify the existing information of the identified item to another system after reading the information, the system Usually running a piece of software between the reader and the application level, often referred to as RFID middleware. Middleware is the link between RFID devices and enterprise applications. It is also the core of the RFID system. The middleware connects the RFID physical devices based on different platforms and different needs, and provides a suitable interface to enable data exchange. According to the different coupling modes of RF signals in RFID systems, it can be divided into inductive coupling and electromagnetic backscatter coupling. Inductive coupling is generally suitable for short-range radio frequency identification systems with medium and low frequency operation. The electromagnetic backscatter coupling method is generally suitable for long-distance radio frequency identification systems operating at UHF and UHF. The specific applications are shown in Table 1.
The Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) is composed of a large number of micro sensor nodes deployed in the monitoring area to form a multi-hop self-organizing network system through wireless communication. Each sensor node in the network has data collection and routing data to The function of the coordinator. The purpose is to collaboratively perceive, collect, and process information about the perceived objects in the network coverage area and send them to the observer. Sensors, sensing objects, and observers form the three elements of a wireless sensor network. The sensor node is generally composed of a function module that collects information, a signal sensor unit, a processing and storage unit, a transceiver unit, a power supply unit, and related support software. A self-organizing network is a reconfigurable multi-hop network without the support of a predetermined infrastructure. The network topology, channel environment, and business mode dynamically change with the movement of nodes. WSN is also a technology with broad application prospects, which can realize data collection, processing fusion and transmission. Therefore, the technology can monitor, sense and collect information of various environments or monitoring objects in the network distribution area in real time, and the commercialization process is still developing. The continuous development of wireless sensor networks and RFID technology has more and more similarities in technology. It can be seen that the combination of wireless sensor network technology and RFID has practical application significance, which will provide more opportunities and space for the upcoming Internet of Things era. It has great economic and social significance, such as the combination of RFID and temperature, humidity or acceleration sensors. Use, not only can monitor the transportation of goods, but also send information such as storage temperature not up to standard and food expiration during transportation to the monitoring center through the information network; relevant information of the truck carrying the goods too fast will also be captured by the acceleration sensor Upon arrival, the monitoring center will alert the truck driver after receiving the information, and even control the truck speed to a normal level through the control information.
3 Fusion WSN RFID systemNetwork Accessories,Wifi Adapter,Fiber Optic Network Components,Splitter Fiber Optic
Cixi Dani Plastic Products Co.,Ltd , https://www.dani-fiber-optic.com