The main problem that NFC mobile phones need to solve near-field communication through CCID interface is to extend the function of CLF in ISO14433 specification, so that CLF supports CCID, and develops this function of CLF from standard terminal into NFC mobile phone standard.
The NFC mobile phone with the SWP SIM card is a combination of the current international specifications. The SWP SIM card requires the support of the NFC mobile phone, and the NFC function of the mobile phone is only for the SWP SIM card service. But with the evolution of smart card technology, this may not be the same. Based on the brief analysis and comparison of existing SWP and CCID technologies, this paper proposes a method and principle of NFC mobile phone to complete near field communication through CCID interface, and briefly describes the application of this method to mobile phone SIM card, terminal and terminal. The impact and future work that must be done.
Background
If the SIM card is to take on the responsibility of mobile payment and many mobile network applications, it is best to support non-contact communication and have a large capacity.
To support non-connected communication functions, a large-capacity SIM card must have the following conditions:
(1) Technical specifications of terminals and cards;
(2) Test specifications for terminals and cards;
(3) Test environment of the terminal and card, simulation environment;
The reality is:
(1) There is no non-connected technical specification for large-capacity SIM cards and their terminals. The current common-capacity SWP cards only define ISO/IEC 7816 and SWP interfaces; Unicom's large-capacity SIM cards and terminal technical specifications complete ISO/IEC The definition and use of the USB interface in the 7816, but superimposing the SWP function on top of it, is by no means a simple copy of the international specification, must address the choice of physical interface ("SWP and CCID" or "ISO/IEC 7816, SWP and CCID") Technical channel selection (ISO/IEC 7816, SWP, CCID, large capacity), ISO/IEC 7816, SWP, CCID, and any two or more concurrency difficulties in large capacity;
(2) The existing test specification of the SWP common SIM card with two interfaces, namely ETSI TS 102 694, is carried out by the "FFS-For Fut-ure Study" in the place where the USB interface is involved, and is to be implemented;
(3) Now test the SWP common SIM card, using Com-prion's ICC Spectro, the test content is implemented according to the existing ETSI specifications, and it is developed around ISO/IEC 7816 and SWP interfaces, and the test environment for USB-IC and SWP The simulation environment has yet to be developed.
Therefore, the implementation of SWP high-capacity SIM card is not a simple superposition of hardware, software, and protocol. We need to change the way of thinking and explore a more feasible and more advantageous solution: NFC function is not implemented through SWP protocol.
2. Simple comparison of SWP, 7816, CCID
SWP is the abbreviation of Single Wire Proto-col, which is a single-wire connection scheme based on SIM card C6 pin proposed by Axalto, one of Gemalto's predecessors. It belongs to the physical layer protocol. To put it simply, a data cable is used to communicate the SIM card with the NFC module, and then communicate with the outside through the CLF of the NFC module. When the NFC mobile phone receives the POS data through the CLF front end, it transmits it to the SWP card through the C6 pin. The frequency of the RF field between the CLF and the POS is 13.56MHz, and the communication speed is several, 106, 212, 424, and 847 kbps. Currently, 106 and 212 kbps are mostly used. The SWP specification requires a bit width from 590ns to 10us per bit, and the conversion communication rate is less than 2Mbps.
The ISO/IEC 7816 international specification is a specification that a contact smart card must follow. The ordinary mobile phone SIM card follows this specification in terms of physical and electrical characteristics. The current ISO/IEC 7816 interface transmission rate supported by most mobile phones is on the order of 100 kbps.
The CCID (Integrated Circuit(s) Cards Interface Device chip card inter-face device) specification defines an APDU (Application Protocol Data Unit) packet format and an application protocol on a USB channel. The USB device conforming to the CCID specification can be either a card reader or an integrated device that integrates CCID and smart card functions. It is such an integrated device that conforms to the China Unicom standard large-capacity SIM card.
Microsoft provides and supports CCID drivers on its Windows 2000 and above operating systems, enabling device manufacturers to easily develop devices that conform to the CCID interface standard. At the same time, the CCID interface standard supports PC/SC interface calls, enabling developers to easily develop and operate information security devices. On many other open source operating systems such as Linux, there are also many open source CCID drivers available for developers and User use. Most smartphones that use the Android operating system also support the CCID driver and provide a PC/SC programming interface. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the scope defined by the CCID protocol.
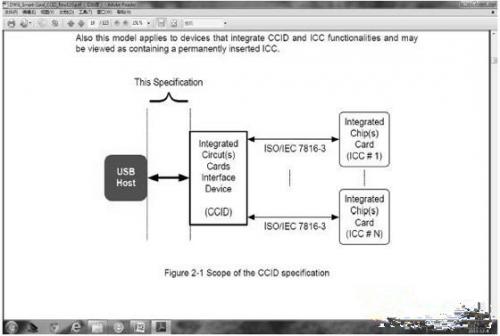
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the scope defined by the CCID protocol
Unicom's upcoming large-capacity SIM card is a USB full-speed device with a bus speed of 12Mbps and supports the CCID protocol. In the future, it is more likely to be upgraded to a USB high-speed interface with a transfer rate of 480 Mbps, or even a full-duplex USB 3.0 with a transfer rate of 5 Gbps.
Printed Circuit Board Assembly
Printed Circuit Board Assembly,High Conductivity Aluminum Substrate,High Precision Pcb Circuit Board,Pcb Processing Circuit Board
Shenzheng Weifu Circuit Technology Co.Ld , https://www.wfcircuit.com