
From audio transmission, graphic transmission, video transmission, to Internet of Things transmission with low power consumption, the Bluetooth application scene is also becoming wider and wider.
The world is blue and unknowingly this world will have 4 billion Bluetooth devices. In this article, we will take you through the technical transition of Bluetooth 1.0 to 5.0, from audio transmission, graphic transmission, video transmission, to Internet of Things transmission with low power consumption. We will also work with you to sort out the increasingly broad Bluetooth application scenario. The past and present you don't know about Bluetooth technology are here.
Perhaps few people know that the word Bluetooth was taken from Harald Bluetooth, the name of Danish king Harald in the tenth century.
The association of "Bluetooth" with later wireless communication technology standards is an engineer from Intel, Jim Kardach. At a wireless communications industry conference, he proposed to use "Bluetooth" as the name of the wireless communication technology standard.

^ The idea of ​​Bluetooth name comes from Intel's Jim Kardach, who was reading historical novels about Vikings and King Harald. | Source: Nordicsemi
Because King Harald is famous for unifying Norway and Denmark, which were divided by religious wars and territorial disputes, the king's achievements coincide with Jim Kardach's ideas. He hopes that Bluetooth can also become a universal universal transmission standard. - Interconnect all distributed devices and content. The LOGO for Bluetooth comes from the post-Fursagram rune combination, which puts together the initials H and B of the name of the Harald King and becomes the blue logo known today.
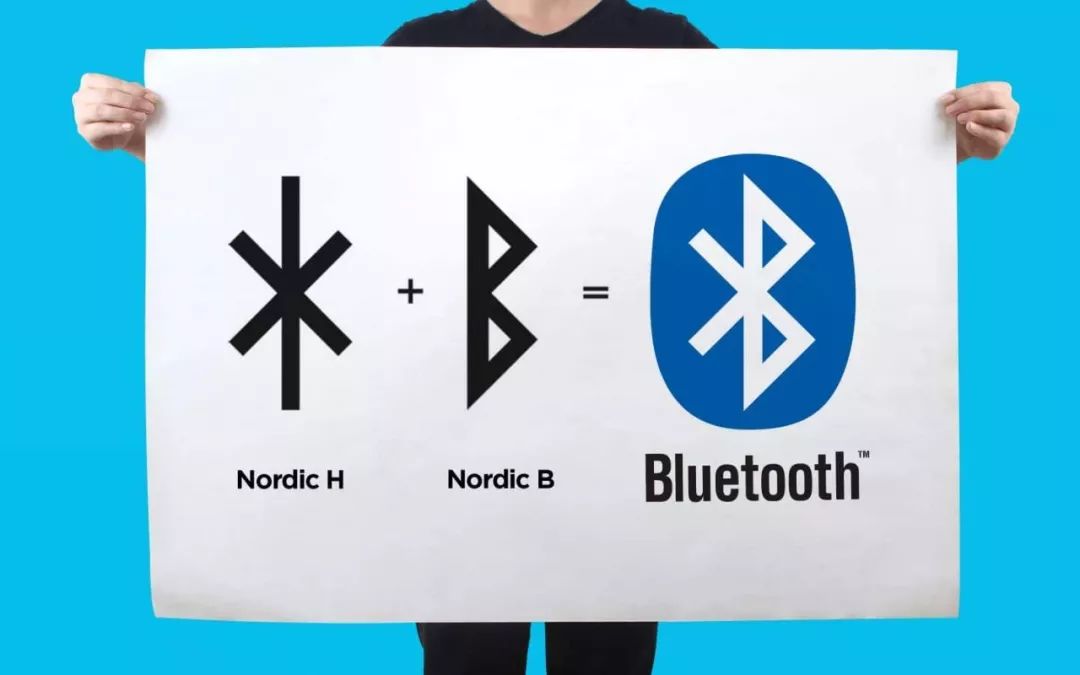
^ Source: Fabrikbrands
People of the year would not have imagined that the application of this blue logo has gone far beyond their intended use scenarios after 20 years. From the use of wireless headphones to receive audio, connect the handle to the game console, and use Apple's "space transfer" to transfer files. Bluetooth has changed from the original high-tech selling point to the standard technology of today's mobile devices and has become an integral part of our lives.
The origin of Bluetooth
The history of Bluetooth actually goes back to World War II. At the heart of Bluetooth is short-range radio communication, which is based on frequency-hopping spread-spectrum (FHSS) technology, presented by Hollywood actress Hedy Lamarr and pianist George Antheil in a patent filed in August 1942. They were inspired by the number of keys on the piano. By using 88 types of radio torpedoes with different carrier frequencies, the transmission frequency is constantly changing, so it has a certain degree of security and anti-jamming capability.
At first, the technology did not attract the attention of the U.S. military. It was not used by the military for wireless communication systems on the battlefield until the 1980s. Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology was later resolved to include Bluetooth, WiFi, and 3G mobile communications. The system plays a key role in wireless data transmission and reception.
Bluetooth technology began with a project created by Ericsson in 1994. It aims to study ways to connect low-power, low-cost wireless communications between mobile phones and other accessories. The inventor hopes to create a set of unified rules (standardized protocols) for the wireless communication between devices to solve the communication problems of incompatible mobile electronic devices among users and to replace the RS-232 serial communication standard.

^ Unforgettable Ericsson of the year | Source: WIKI
Ericsson found that the solution to the compatibility problem was to connect different kinds of communication equipment to the cellular network through the mobile phone. The last paragraph of the connection was a short-range wireless connection. As the project progressed, Ericsson invested a large amount of resources in the research and development of short-range wireless communication technology.
On May 20th, 1998, Ericsson teamed up with 5 well-known companies such as IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba to form the Special Interest Group (SIG), the predecessor of the Bluetooth technology alliance. The goal is to develop a low-cost, Bluetooth technology standard with high efficiency and free wireless connection over a short distance. Bluetooth introduced 0.7 specifications that year, supporting Baseband and Link Manager Protocol (LMP) protocols.
In 1999, it launched the 0.8, 0.9 and 1.0 Draft versions. The SDP (Service Discovery Protocol) and TCS (Telephony Control Specification) agreements have been completed.
The 1.0A version was formally announced on July 26, 1999, and the use of the 2.4GHz band was determined. Compared with the popular infrared technology at that time, Bluetooth has a higher transmission speed, and does not need to connect to the interface as infra-red. All Bluetooth devices can be connected at any time as long as they are used within the effective communication range.
In the second half of 1999, Microsoft, Motorola, Samsung, Lucent, and the five companies in the Bluetooth special group jointly initiated the establishment of a Bluetooth technology promotion organization. This has created a global "Bluetooth" boom.
By April 2000, the number of members of the SIG had exceeded 1,500, and it has grown faster than any other wireless alliance.
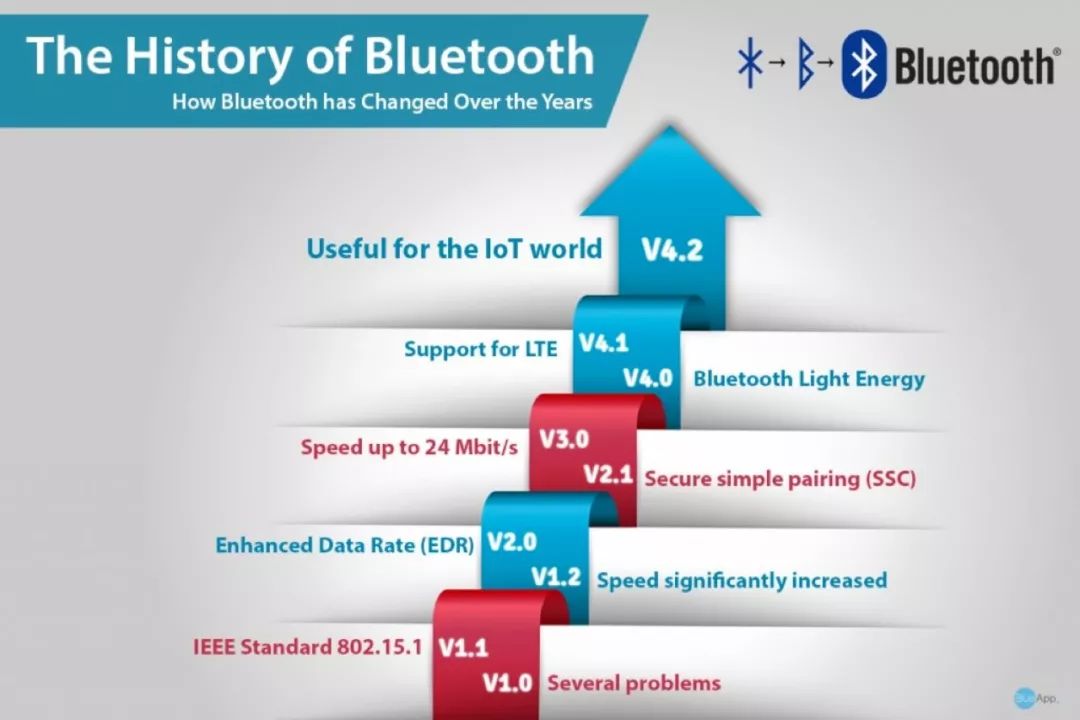
^ History of Bluetooth Technology Changes | Source: BlueAPP
First Generation Bluetooth: Early Exploration of Short-distance Communication
1999: Bluetooth 1.0
There were several problems with the earlier Bluetooth versions 1.0 A and 1.0B, and several vendors pointed out that their products are incompatible with each other. At the same time, during the “handshaking†of the two devices, the Bluetooth hardware address (BD_ADDR) is sent out, which cannot be anonymous at the protocol level, posing a risk of data leakage.
Therefore, when the 1.0 version was introduced, Bluetooth was not immediately applied widely. In addition to the small number of electronic devices corresponding to Bluetooth functions at the time, Bluetooth devices are also very expensive.
2001: Bluetooth 1.1
Bluetooth version 1.1 is formally included in the IEEE 802.15.1 standard, which defines the physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) specifications for wireless connectivity between devices with a transmission rate of 0.7 Mbps. However, because of its early design, it is vulnerable to product interference between the same frequency and affects the communication quality.
2003: Bluetooth 1.2
Bluetooth version 1.2 addresses the security issues exposed by version 1.0, completes the anonymous approach, adds the Shielded Device Hardware Address (BD_ADDR) feature, protects users from identity sniffing attacks and tracking, and is backward compatible with version 1.1. In addition, four new features have been added:
AFH (Adaptive Frequency Hopping) adaptive frequency hopping technology reduces the interference problem between Bluetooth products and other wireless communication devices;
eSCO (Extended Synchronous Connection-Oriented links) extends synchronous link-oriented channel technology to provide QoS audio transmission to further meet the requirements of high-end speech and audio products;
The fast connection function of Faster Connection can shorten the time for re-searching and reconnecting, making the connection process more stable and faster.
Supports transmission requirements for Stereo sound effects, but only works in simplex mode.

^ Masterpiece: Ericsson's first Bluetooth mobile phone T39mc | Source: WIKI
Second generation Bluetooth: EDR era of transmission rate
2004: Bluetooth 2.0
Bluetooth 2.0 is a modified version of the 1.2 version. The newly added EDR (Enhanced Data Rate) technology enables the transmission rate of Bluetooth devices to reach 3Mbps by improving the ability of multi-tasking and multiple Bluetooth devices to run simultaneously.
Bluetooth 2.0 supports duplex mode: It allows voice communication while transferring documents/high-quality pictures.
At the same time, EDR technology reduces power consumption by reducing the working-liability cycle, and Bluetooth 2.0 increases the number of connected devices due to increased bandwidth.
2007: Bluetooth 2.1
Bluetooth 2.1 has added the Sniff Subrating power-saving function to extend the interval between device-to-device communication confirmations from 0.1 seconds to 0.5 seconds, which greatly reduces the workload of the Bluetooth chip.
In addition, the new SSP Easy Security Pairing feature improves the pairing experience of Bluetooth devices while increasing usage and security.
Supports NFC near field communication, as long as two Bluetooth devices with built-in NFC chip are brought close to each other, the pairing password will be transmitted through NFC without manual input.

^ Masterpiece: Sony Ericsson P910i PDA phone with Bluetooth and wireless headsets | Source: WIKI
Third generation Bluetooth: High Speed, transmission rate up to 24Mbps
2009: Bluetooth 3.0
Bluetooth 3.0 adds optional technology High Speed, High Speed ​​enables Bluetooth to call 802.11 WiFi for high-speed data transfer, transfer rate up to 24Mbps, 8 times that of Bluetooth 2.0, easy to implement VCR to HDTV, PC to PMP, UMPC Data transfer between printers.
The heart of Bluetooth 3.0 is AMP (Generic Alternate MAC/PHY), a new alternative radio technology that allows the Bluetooth stack to dynamically select the correct radio for any task.
In terms of power consumption, Bluetooth 3.0 introduces EPC enhanced power control technology, supplemented by 802.11, and the actual idle power consumption is significantly reduced.
In addition, the new specification also adds UCD one-way broadcast connectionless data technology to improve the corresponding capabilities of Bluetooth devices.

^ Masterpiece: Bluetooth adapter | Source: Future World Network
The fourth generation of Bluetooth: The main push "Low Energy" low power
2010: Bluetooth 4.0
Bluetooth 4.0 is the first Bluetooth integrated protocol specification to date, integrating the three specifications. One of the most important changes is the low-power BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) function, which proposes low-power Bluetooth, traditional Bluetooth, and high-speed Bluetooth:
"High-speed Bluetooth" focuses on data exchange and transmission; "traditional Bluetooth" focuses on information communication and device connection; "Low-power Bluetooth" connects mainly to devices that do not occupy too much bandwidth, and its power consumption is lower than that of the old version. 90%.
BLE is the predecessor of the Wibree technology developed by NOKIA. It was originally developed as a very low-power mobile wireless communication technology developed for mobile devices. After being accepted and standardized by SIG, it was renamed Bluetooth Low Energy (hereinafter referred to as Bluetooth Low Energy). ). These three protocol specifications can also be combined with each other to achieve a wider range of application models.
Bluetooth 4.0 chip mode is divided into Single mode and Dual mode. Single mode only works with Bluetooth 4.0 and cannot be down-compatible with 3.0/2.1/2.0; Dual mode is backwards compatible with 3.0/2.1/2.0. The former is applied to sensor devices that use button batteries, such as heart rate detectors and thermometers that require high power consumption; the latter is applied to conventional Bluetooth devices while taking into account the need for low power consumption.
In addition, Bluetooth 4.0 also increases Bluetooth's transmission distance to more than 100 meters (under low-power mode conditions). Has a faster response time, the minimum can be completed in 3 milliseconds connection settings and start transmitting data. The more secure technology uses AES-128 CCM encryption algorithm for packet encryption and authentication.

^ Masterpiece: Apple's iPhone 4S is the first smartphone to support the Bluetooth 4.0 standard | Source: Quora
2013: Bluetooth 4.1
Bluetooth 4.1 has a small change in transmission speed and transmission range, but there are significant improvements in software. The purpose of this update is to make Bluetooth Smart technology the ultimate driving force for the development of the Internet of Things.
Support seamless collaboration with LTE. When Bluetooth and LTE radio signals transmit data at the same time, then Bluetooth 4.1 can automatically coordinate the transmission information of both to ensure coordinated transmission and reduce mutual interference.
Allows developers and manufacturers to "customize" the reconnection interval of Bluetooth 4.1 devices, giving developers greater flexibility and control.
Supports "cloud synchronization." Bluetooth 4.1 has added a dedicated IPv6 channel. Bluetooth 4.1 devices only need to connect to devices that can be networked (such as mobile phones), and can synchronize data with the cloud through IPv6 to meet the application requirements of the Internet of Things.
Supports the interchange of "extended equipment" and "central equipment" roles. Earphones, watches, and mice, which support the Bluetooth 4.1 standard, can transmit and receive data without using data hubs such as PCs, tablets, and mobile phones. For example, smart watches and pedometers can bypass smart phones and directly implement dialogues.
2014: Bluetooth 4.2
The Bluetooth 4.2 transmission speed is faster, 2.5 times faster than the previous generation, because the capacity of the Bluetooth Smart (Bluetooth Smart) data packet is increased, and the amount of data that can be accommodated is equivalent to about 10 times.
Improve the transmission rate and privacy protection, Bluetooth signals want to connect or track user equipment must be user license. Users can feel comfortable using wearable devices without worrying about being tracked.
6LoWPAN is supported, and 6LoWPAN is a low-speed wireless personal area network standard based on IPv6. Bluetooth 4.2 devices can access the Internet directly via IPv6 and 6LoWPAN. This technology allows multiple Bluetooth devices to access the Internet or local area network through a single terminal. In this way, most smart home products can abandon relatively complicated WiFi connections and switch to Bluetooth transmissions, making the interconnection between personal sensors and families more convenient and faster.
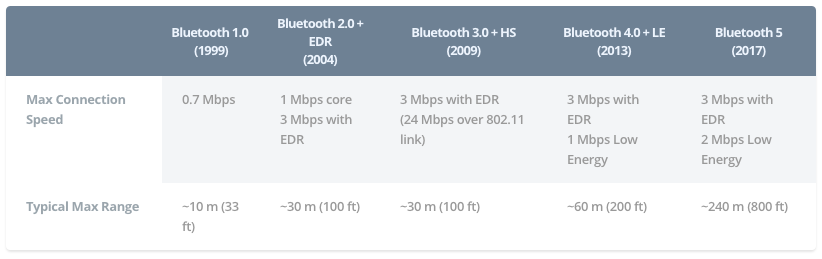
^ Bluetooth standard performance | Source: Android Authority
Fifth Generation Bluetooth: Opening the Door to the Internet of Things
2016: Bluetooth 5.0
Bluetooth 5.0 has faster and longer transmission capability in low-power mode, twice the transmission rate of Bluetooth 4.2 (up to 2 Mbps in speed), effective transmission distance is four times that of Bluetooth 4.2 (300 meters in theory), Packet capacity is eight times that of Bluetooth 4.2.
Support indoor positioning and navigation functions, combined with WiFi can achieve indoor positioning accuracy less than 1 meter.
The underlying optimization of the IoT IoT is aimed at providing smart home services with lower power consumption and higher performance.
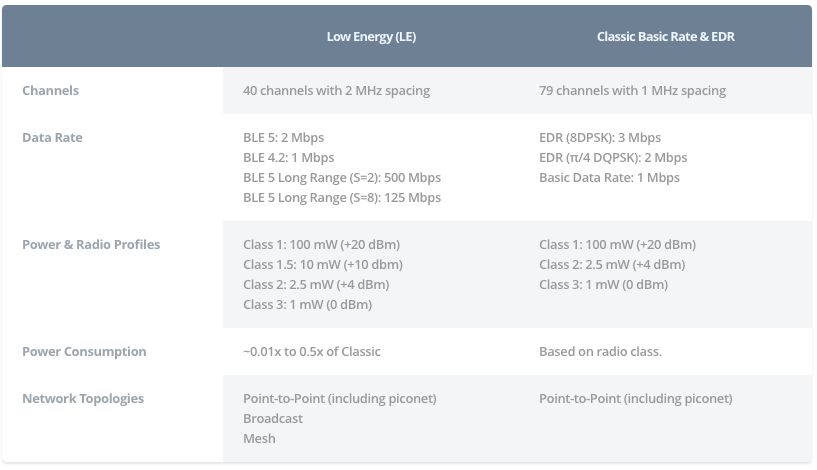
^ Low-power Bluetooth and classic Bluetooth parameters | Source: Android Authority
Mesh Mesh Network: The Key to Realize the Internet of Things
The Mesh mesh network is an independently developed network technology that can use Bluetooth devices as signal relay stations to cover data in very large physical areas and is compatible with Bluetooth 4 and 5 series protocols.
The traditional Bluetooth connection is achieved through the "pairing" of one device to another device, establishing a "one-to-one" or "one-to-many" micro-network relationship.
The Mesh network enables devices to achieve "many-to-many" relationships. Each device node in the Mesh network can send and receive information. As long as one device is connected to the gateway, the information can be relayed between the nodes so that the message can be transmitted to a location farther than the normal radio wave transmission distance.
In this way, the Mesh network can be distributed in manufacturing plants, office buildings, shopping malls, business parks, and wider scenes to provide more stable control solutions for lighting equipment, industrial automation equipment, security cameras, smoke detectors, and environmental sensors.
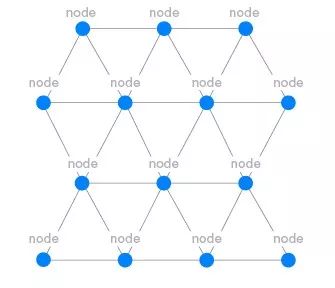

^ Mesh network in office building | Source: Buletooth
Internet of Things: The New Home of Future Bluetooth Technology
Since 1998, the Bluetooth protocol has been updated several times, from audio transmission, graphic transmission, video transmission, to Internet of Things data transmission with low power consumption. While maintaining the backward compatibility of Bluetooth devices, on the other hand Bluetooth is also being applied to more and more IoT devices.
With the increasing power consumption and transmission efficiency of Low Energy Bluetooth, the Classic version has not been updated since 3.0. It can be foreseen that the main force of Bluetooth in the future will be focused on the Internet of Things, not just on mobile devices. The addition of the Mesh mesh network makes it possible for Bluetooth to become an IoT system.
According to SIG's market report, by the end of 2018, global Bluetooth device shipments will reach as much as 4 billion, of which: shipments of mobile phones, tablets and PCs will reach 2 billion this year, and shipments of audio and entertainment devices will reach 12 Billion, 86% of the globally-manufactured cars will have Bluetooth capabilities, and the shipment of smart home Bluetooth devices will reach 650 million. Intelligent buildings, smart cities, smart industries, etc. will all become future potential tracks.
With the advent of Bluetooth 5 technology and the maturity of Bluetooth mesh technology, the long-distance and multi-device communication thresholds between devices have been greatly reduced, which has brought greater imagination to the future IoT. This technology, which was introduced 20 years ago, will continue to flourish in the future.
1. 4-IN-1 MOBILE CONTROLLER mobile game controller which combines Gaming Triggers, Silent cooling fan, Emergency charging bank and charging cable in order to improving and promoting your immersive gaming experience, which also could help you get a good score in the shooting games.
2. COOLING FUNCTION & EMERGENCY CHARGING .mobile game controller with a built-in silent cooling fan and a high quality 1200mAh battery, the built-in silent cooling fan could help cooling your hot mobile phone, and 1200mAh battery also could help charging your mobil phone when your mobile phone is almost powered off.
3. PLAYING WITH 4 FINGERS - Customize the button as you like, you can play shooting games with 6 fingers, such as aiming, shooting, moving, squatting, left tilted head and right tilted head at the same time. In addition, the turnover button can help you customize icon more easily.
4. SUPPORTED DEVICES & GAMES - Suitable for the majority of mobile phone, the max stretch width is 3.9inchwhich could compatible with the majority of shooting games, such as Rules of Survival, Knives Out, Survivor Royale, Critical Ops, etc.
5. EXCELLENT SERVICE - If our Mobile Game Controller have any problems, please contact us by email, we will replace the defective product for you as soon as possible, and we offer 12 months warranty.
Mobile Game Controller,Game Pubg Controller,Gamepad Equipment,Game Shooter Controller
MICROBITS TECHNOLOGY LIMITED , https://www.hkmicrobits.com