Introduction
USB 3.0 can achieve this new level of performance without changing the waveform factor of the USB connector in the PC, and is fully backward compatible in all other respects. This article provides an introduction to USB 3.0 and various factors that affect the application of USB 3.0. Although our focus here is on memory applications, we are also involved in some other applications, because the versatility of USB is the main reason for using this interface with external disk drives.
For storage applications, assuming that they are used as interfaces for external and internal storage, respectively, the relationship between USB and SATA is particularly interesting. Since the current USB 3.0 can support the highest conversion rate of the disk drive, to a large extent, the general-purpose SATA drive can be used as an external USB 3.0 peripheral. By using a device capable of bridging USB3.0 and SATA, it is the most direct way to add the USB 3.0 interface to the SATA drive.
According to market demand, Fujitsu has launched the world's first highly integrated USB3.0-SATA bridge chip. Using a form factor that can be easily matched with existing systems, the chip greatly simplifies the implementation of external hard drives on PC and Mac platforms, and provides transparent data transmission between USB3.0 ports and external disk drives. Therefore, this device helps to utilize USB applications that have turned to external SATA (eSATA) for performance reasons, allowing drive manufacturers to easily take advantage of the universal connectivity promised by USB 3.0.
Introduction to USB 3.0
USB 3.0-also known as SuperSpeed ​​USB-provides a standard interface for various devices connected to PCs or audio / high-frequency devices. From keyboards to high-throughput disk drives, a variety of devices can use this low-cost interface for smooth-running plug-and-play connections, and users do n’t need to worry too much about it. While maintaining compatibility with USB 2.0, the new USB 3.0 also provides the following enhancements:
Greatly improved bandwidth-up to 5Gbps full duplex (USB2.0 is 480Mpbs single duplex)
Achieve better power management
It enables the host to provide more power to the device, enabling applications such as USB-rechargeable batteries, LED lighting, and mini fans.
Can make the host identify the device faster
New protocol makes data processing more efficient
USB 3.0 can transfer large-capacity files (such as HD movies) at the storage rate defined by the storage device. For example, a flash drive using USB 3.0 can transfer 1GB of data to a host in 3.3 seconds, while USB 2.0 takes 33 seconds.
Driven by the ever-increasing demand for resolution and storage performance of consumer electronics devices, it is hoped that wider media applications can be achieved through broadband Internet connections. Therefore, users need faster transmission performance to simplify downloading, storage, and mass multimedia Content sharing. USB 3.0 has played a vital role in providing consumers with the simple connectivity they need.
When used in consumer devices, USB 3.0 will solve the problem that USB 2.0 cannot recognize batteryless devices. The host can slowly reduce the current through USB 3.0 to identify these devices, such as a mobile phone with a broken battery.
For system and ASIC developers, the wide availability of USB 3.0 chips and IP ensures that every design requirement can be met in time. This comprehensive support is particularly important for standards like USB 3.0, because speed, advanced protocols, and various cable lengths (from a few inches to a few meters) make design and standard compatibility a challenge.
SATA and USB
In recent years, among the various devices competing to become external memory interfaces, USB, eSATA, and Firewire have each achieved many remarkable achievements in the field of personal computers. At this point, Serial ATA (SATA) replaces all other interfaces in the internal drive connectivity of consumer PCs. Although the new CompactFlash version called CFast will be built on SATA, the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) continues to be used in industrial and embedded applications that use CompactFlash as a storage medium.
Since its launch in 2004, eSATA has challenged USB 2.0 and FireWire in external memory applications. eSATA transfers data with external devices at the same rate supported by SATA internal drives. It is worth mentioning that the eSATA interface can support data transfer rates up to 3Gbps. Even after taking into account the actual rate reduced by the encoding, the data rate of eSATA is completely sufficient to be used as the highest-speed hard disk drive, which can transfer data at a rate of 120 / sec (about 90Mbps).
Although eSATA is only used for memory applications, these features enable it to seize the market share of USB 2.0 and FireWire. Other advantages of SATA include low processor cost. The performance of USB 3.0 is significantly better than eSATA and FireWire 800. At 5Gbps full duplex, USB 3.0 is faster than eSATA and FireWire 800, which can reach 800Mbps full duplex. (Note that eSATA's 3Gbps data is single-duplex, and USB 3.0 provides full-duplex. Although we cannot elaborate here, we still need to note that USB 3.0 includes optional devices for Transmission of disordered data is the best choice for disk drive search.)
Fujitsu's USB 3.0-SATA chip solution
In order to implement a simple method that can use SATA hard drives for USB 3.0, Fujitsu has introduced the MB86C30A single-chip solution to bridge USB 3.0 and mass storage based on SATA / ATA / ATAPI. This bridge chip transfers USB2.0 and USB3.0 mass storage requirements to SATA and ATA / ATAPI communication protocols.
MB86C30A is the world's first USB 3.0 slave chip, which uses Fujitsu's high-speed serial I / O technology. In the near future, chips built with 65nm CMOS technology will achieve lower power consumption and greater flexibility in adopting high-speed USB specifications. Fujitsu has demonstrated its USB 3.0 slave chip at the "2009 SuperSpeed ​​USB Developer Conference" and proved that it has the fastest transfer rate in the industry.
This chip meets the requirements of USB 3.0 specification 1.0 and SATA specification 2.6 released in November 2008. The chip also conforms to the USB Mass Storage bulk transfer protocol. Figure 1 shows the main functions of the chip.
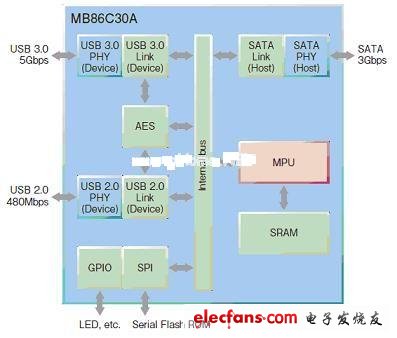
Figure 1: Fujitsu's MB86C30A USB3.0-SATA bridge chip
MB86C30A main features
High-speed encryption engine
In terms of security, the MB86C30A embedded command parser supports the ATA command set, with a high-speed encryption engine and DMA controller. Because the encryption function is controlled by hardware rather than software, MB86C30A maximizes the potential transfer rate of USB 3.0 (see Figure 2). The chip supports 128-bit and 256-bit main lengths for CBC-AEC and XTS-AES. The encryption engine is a standard AES code / decoding hardware engine based on the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Smart meter is one of the basic equipments for data acquisition of smart grid (especially smart distribution network). It undertakes the task of collecting, measuring and transmitting raw energy data, and is the basis for information integration, analysis optimization and information presentation. In addition to the metering function of the basic power consumption of the traditional electric energy meter, the smart meter has two-way multi-rate metering function, user-side control function, and two-way data communication in various data transmission modes in order to adapt to the use of the smart grid and new energy. Intelligent functions such as function and anti-stealing function
Meter Pcb,Pcb Circuit Boards,Pcb Circuit Board For Meter,Multilayer Printed Circuit Board
Chuangying Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.cwpcb.com