Modern society's reliance and requirements on communication are getting higher and higher, so the design and development of more efficient communication systems has become the goal pursued by the communication engineering community. The efficiency of the communication system is, in the final analysis, spectrum utilization and power utilization. Especially in the case of wireless communication, the utilization of the two indicators is higher, especially the spectrum utilization. As a result, various communication technologies with higher spectral efficiency have been continuously developed. OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division MulTIplexing, Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) is a special multi-carrier modulation technology that uses the orthogonality between carriers The performance further improves the spectrum utilization, and can resist narrow-band interference and multi-menstrual fading. OFDM transmits serial data in parallel through multiple orthogonal subcarriers, which can increase the width of the symbol, reduce the frequency band occupied by a single symbol, resist frequency-selective fading caused by multipath, and can effectively overcome crosstalk between symbols and reduce The system's requirement for equalization technology is one of the main technologies supporting future mobile communications, especially mobile multimedia communications.
1 Basic principles of OFDM
The principle of a complete OFDM system is shown in Figure 1. The basic idea of ​​OFDM is to modulate serial data on multiple orthogonal subcarriers in parallel, which can reduce the symbol rate of each subcarrier, increase the symbol period of the symbol, and improve the system's ability to resist fading and interference At the same time, due to the orthogonality of each subcarrier, the spectrum utilization rate is greatly improved, so it is very suitable for high-speed transmission in mobile occasions.
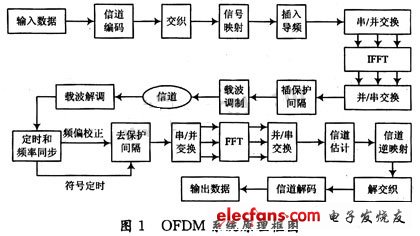
At the sending end, the input high bit stream generates a modulation signal through modulation mapping, which is converted into N parallel low-speed sub-data streams through serial-to-parallel conversion. Each N parallel data constitutes an OFDM symbol. After inserting the pilot signal, the N data of each OFDM symbol is modulated by inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), and the time domain signal becomes:
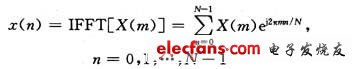
Where: m is a discrete point in the frequency domain; n is a discrete point in the time domain; N is the number of carriers. In order to effectively suppress InterSymbol Interference (ISI) at the receiving end, a Guard Interval (GI) is usually added before each time-domain OFDM symbol. The signal after adding the guard interval can be expressed as formula (2), and finally the signal undergoes parallel / serial conversion and D / A conversion and is sent out by the transmitting antenna.

The receiving end processes the received signal to complete timing synchronization and carrier synchronization. After A / D conversion, the signal after serial-to-parallel conversion can be expressed as:
yGI (n) = xGI (n) * h (n) + z (n) + w (n) (3)
Then, after removing the CP, perform FFT demodulation and channel estimation (according to the inserted pilot signal), and then send the channel estimation value and the FFT demodulation value to the detector for coherent detection, and detect the The information symbol is finally recovered by de-mapping and channel decoding. After removing the cyclic prefix (CP), the FFT transformed signal can be expressed as:
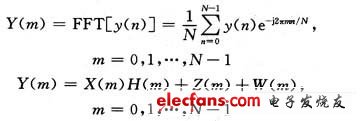
Where: H (m) is the Fourier transform of the channel h (n); Z (m) is the Fourier transform of the inter-symbol interference and inter-carrier interference z (n); W (m) is the additive Gaussian white Fourier transform of noise w (n).
2 OFDM system implementation model
An OFDM system implemented using discrete inverse Fourier transform (IDFT) or fast inverse Fourier transform (IFFT), as shown in Figure 2.
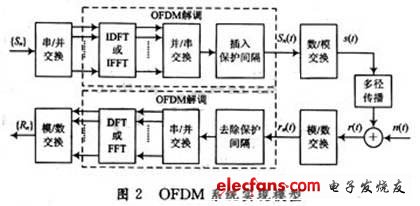
It can be seen from the implementation model of the OFDM system that after the input complex signal has undergone serial / parallel conversion, IDFT or IFFT and parallel / serial conversion are performed, and then the guard interval is inserted, and then subjected to digital / analog conversion to form OFDM modulation Signal s (t). After the signal passes through the channel, the received signal r (t) undergoes analog-to-digital conversion, removes the guard interval to restore the orthogonality between the subcarriers, and then undergoes serial / parallel conversion and DFT or FFT to recover OFDM The modulated signal of the input signal is restored after parallel / serial conversion.
The Glass Convection heater warm the room as it passes over a heated coil; some use a fan to forced in the cool air to heat. The heated air rises naturally or is forced out by a fan and spreads into the space to warm room.
A Glassl convection heater is a type of heater that uses convection currents to heat and circulate air. These currents circulate throughout the body of the appliance and across its heating element.
Glass Convector Heater including glass convection heater, Metal Convection Heater, also mini Convector Heater can be a Frost Heater.
welcome to OEM,thank you
Glass Convector Heater
Glass Panel Convector Heater,Electric Convector Panel Heater,Mounted Glass Panel Convector Heater,Glass Panel Heater Convector Heater
Fenry manufacturing Co., Ltd , https://www.cnfenry.com