In 1998, Philips, Sony and Nokia created the NFC Forum, which aims to promote the development and standardization of NFC. The Forum has launched a total of five categories of technical specifications: Protocol Technical SpecificaTIon; Data Exchange Format Technical SpecificaTIon; NFC Forum Tag TypeTechnical SpecificaTIons; Record Type Definition Technical Specification (Record Type DefiniTIonf Technical Specifications); Reference Application Technical Specifications. This article will introduce the first four points of the technology development.
I. Protocol technical specifications
The NFC Forum's protocol specification also includes three technical specifications, namely:
1. NFC Logical Link Control Protocol (LLCP) Technical Specification: defines the Layer 2 protocol of the OSI model to support peer-to-peer communication between two NFC-enabled devices. LLCP is a compact protocol based on the industry standard IEEE802.2 designed to support limited data transfer requirements such as small file transfers or network protocols, which in turn provides a reliable service environment for applications. NFC's LLCP provides a solid foundation for peer-to-peer applications compared to the ISO IIEC18092 standard, but the former enhances the basic functionality provided by the latter without affecting the interoperability of legacy NFC applications or chipsets. .
2. NFC Digital Protocol Specification: This specification emphasizes the digital protocol used for NFC device communication and provides an implementation specification based on the ISO I IEC 18092 and ISO I IEC 14443 standards. The specification defines a common set of features that can be used for major NFC technology applications such as financial services and public transportation without further modifications. It also covers the digital interfaces used by NFC devices as initiators, targets, readers, and card emulators, as well as protocols for half-duplex transmission. NFC devices can use the bit-level coding, bit rate, frame format, protocol, and command set given in this specification to exchange data and bind to the LLCP protocol.
3. NFC Activity Specification: This specification explains how to use the NFC Digital Protocol Specification to establish communication protocols with another NFC device or NFC Forum tag. The Reference Application Specification includes the NFC Forum Connection Handover Technical Specification, which defines the structure and interaction sequences used to establish a connection between two NFC devices using other wireless communication technologies. On the one hand, the specification allows developers to choose the carrier to exchange information, such as Bluetooth or WiFi to exchange data between two NFC phones; on the other hand, NFC-compatible communication devices can be defined in the NFC data exchange format during the connection establishment phase. The required information carried in the message.
Second, NFC Data Exchange Format Technical Specification (NDEF)
NDEF, a message encapsulation format that defines the transfer of data between NFC devices and between devices and tags. The protocol considers that information transmitted between devices can be encapsulated into an NDEF message, and a message can be composed of multiple NDEF records, as shown in the figure.
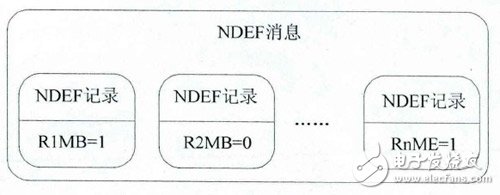
A single NDEF record contains multiple header fields and payload fields. The header contains five flag bits (MB, ME, CF, SR, IL), tag type classification TNF, length information for variable length regions, type identification bits, and an optional record identifier (ID). As shown in the table. In the above figure, R1 to Rn indicate that there are n records, where the MB bit value of R1 is 1 to indicate the start of a message, the ME bit of Rn is 1 to indicate the end of the message, and the two bits of the intermediate record are 0.
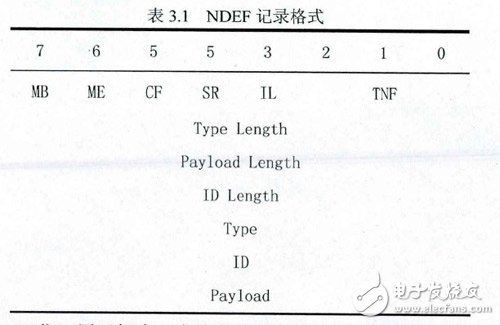
MB and ME bits: A record used to mark the start and end of a message.
A CF value of 1 indicates the presence of the next record.
The SR defines the length of the payload field (Payload). A value of 0 indicates that the size of the Payload Length field is a 4-byte unsigned integer. A value of 1 represents an unsigned integer of one byte. This flag is used to reduce memory waste for short recordings.
If IL is 1, you need to give the value of the optional ID field and its associated length field.
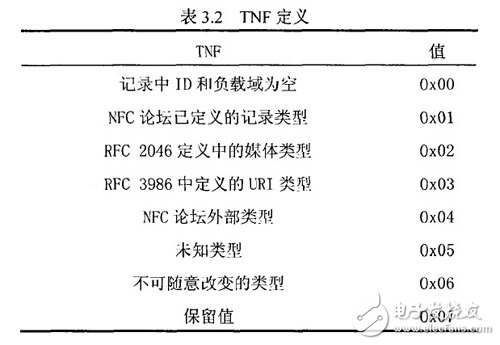
The definition of TNF (Type Name Format) is shown in the table below.
Dongguan Guancheng Precision Plastic Manufacturing Co., Ltd. , https://www.dpowerchargers.com