Recently, the opening records of Huazhu's hotels were leaked. The leaked data involved 130 million users. For a while, how to protect the user's information security became the focus of social discussion.
Have you ever remembered that two years ago, a photo of Zuckerberg on Facebook attracted the attention of netizens around the world. Zuckerberg used tape to cover his computer's camera and microphone to prevent information leakage.

With the large-scale popularization of smart devices and the Internet, the risk and frequency of cyber attacks by users and enterprises is increasing.
According to research data from RiskIQ, a US cybersecurity company, 1.5 organizations worldwide are attacked by ransomware every minute, and companies lose an average of US$15,221. Using the Internet to describe the severity of hacking in one minute, data shows that cybercrime can cause losses of US$1,138,888 in one minute.
In daily life, products such as computers, mobile phones, and smart home appliances are all vulnerable to various forms of attacks, resulting in loss of digital assets and data leakage.
Nowadays, data leakage is impossible to prevent. Modern hackers can attack the network and steal data from various unexpected places.
1. Use the microphone to monitor the contents of the mobile phone screen
Ultrasonic tracking technology can push various location services to users' smartphones, but unsupervised ultrasonic technology may become a very big security risk.
At this year's Crypto 2018 conference, a research team found that it can accurately interpret the contents of the display screen by monitoring and analyzing the ultrasonic waves emitted by the LCD display, and using machine learning technology to analyze these sounds.
For some zebra patterns and websites, researchers have a 90-100% success rate.
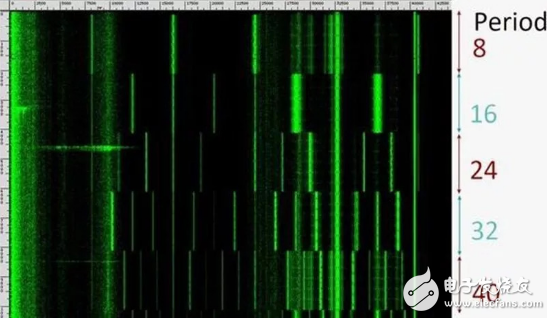
The researchers also found that both webcams and smartphone microphones can be used to extract the sound from the screen to monitor the user's smartphone.
2. Use fish tank thermometer to steal casino database
With more and more networked devices, these devices have also become an important way for hackers to invade corporate networks, especially small devices that are easily overlooked.
The network security company Darktrace once analyzed a hacking incident. The hacker entered the casino network through a networked thermometer in the aquarium of a casino, and transmitted an important database to the cloud.
3. Use sound to destroy mechanical hard drives
In September 2016, Romanian ING Bank conducted a fire extinguishing test at the Bucharest data center. The loud noise caused by the inert gas released during the test caused severe damage to dozens of hard drives and interrupted bank services for 10 hours.

At the 39th IEEE Security/Privacy Symposium, researchers from the Michigan and Zhejiang University teams discovered that using sound attacks can make mechanical hard drives go on strike. At the scene, the researchers used an adapted Katy Perry song to make the Windows 10 laptop blue screen directly, prompting the hard disk error.
4. Use computer fan sound to steal data
A research team from the Cyber ​​Security Research Center of Ben Gurion University in Israel discovered that the sound of a computer cooling fan can steal data.
The research team developed a malware called "Fansmitter". Based on the principle that data is a combination of 0 and 1, after infecting the computer, it will control the fan speed to make it work at two different speeds, corresponding to the binary " 1", "0", thereby stealing computer data.
This attack method can be applied to systems without sound hardware or speakers, such as servers, printers, IoT devices, and industrial control systems.
5. Steal data through computer cooling
A computer that is completely disconnected from the Internet is considered a relatively safe computer, but hackers can use the computer to dissipate heat and do not need to insert any physical devices to remotely read the data in the computer.

The research team of the Cyber ​​Security Research Center of Ben Gurion University in Israel found that it can read the heat emitted by the computer processor, from the isolation gatekeeper type computer (isolated gatekeeper, air-gapping, a kind of use of dedicated hardware to make two or more In the case of disconnection, the network can achieve secure data transmission and resource sharing technology) to obtain data.
6. Send a fax to hack into the network
Although fax machines are not as popular anymore, and fax machines have been designed to print and fax all-in-one machines to connect to the office network. However, there are still 300 million fax numbers and 45 million fax machines in use around the world. In some commercial fields, fax is still very popular.
The Check Point malware research team found that only a fax number is needed to send an image file containing malicious information by fax. Once the fax machine receives the image file, the image will be decoded and uploaded to the fax machine’s memory, using the communication protocol Two serious remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities in the vulnerabilities can invade the enterprise or home network.
7. The brightness of smart bulbs can leak data
Recently, researchers at the University of Texas at San Antonio have proposed a new technology to analyze the brightness and color of smart bulbs from a distance to obtain user data.
When users listen to music and watch videos in a house with smart bulbs, the brightness and color of the linked smart bulbs will change slightly with the level of sound. The visible light and infrared spectra emitted by the smart bulbs can be captured by the device. decoding.
Through experiments, it is found that as the distance becomes longer, the quality of the image obtained by the analysis becomes correspondingly worse, but effective information can still be obtained at a distance of 50 meters.
8. Monitor your phone by voice
In March 2017, researchers from the University of Michigan and the University of South Carolina discovered that sound waves can be used to invade smartphones.

Researchers have found that using sound waves of a specific frequency can cause the accelerometer (a sensor) on the mobile phone to resonate, allowing it to receive wrong information, thereby controlling the mobile phone system. South Korean researchers have used similar methods to invade drones.
In short, while the Internet is advancing with leaps and bounds, we can never slack off the accompanying network security issues. Always remain vigilant, strengthen protective measures, and adhere to good usage habits.
With the rapid development of wireless sensing technology, 433 MHz wireless communication devices have been more widely used in portable devices, vehicle-mounted terminals, intelligent locks and other fields [1]. As an important part of wireless communication equipment, antenna is a key component that affects the overall performance of the communication system [2].
Domestic and foreign scholars have been exploring the 433 MHz printed antenna with high gain and miniaturization for many years. However, there are two main trends in the design of 433 MHz printed antenna by previous scholars: one is to sacrifice size to ensure high gain, such as the structural scheme in literature [3]; The other is to sacrifice gain to ensure size miniaturization, such as the scheme in reference [4].
Taking into account the effective size and gain characteristics of the antenna is the difficulty in the design of 433 MHz miniaturized printed antenna. Based on the research experience of domestic and foreign scholars on 433 MHz printed antenna, a 433 MHz miniaturized spiral printed antenna is designed based on the 1/4 wavelength monopole antenna. The simulation results show that the antenna occupies only 20×35 mm2 and the effective gain is -4.14 dB.
433MHZ Rubber Antenna,433Mhz Patch antenna,433MHZ antenna with magnetic base,433MHZ Yagi Antenna
Yetnorson Antenna Co., Ltd. , https://www.yetnorson.com