Today, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are the fastest growing automotive applications. According to market research firm Gartner's report, the scale of ADAS will grow from $5.6 billion in 2014 to $10.2 billion in 2018, achieving a compound annual growth rate of 17.1% between 2013 and 2018, and the consumption of related semiconductor products. At the same time, it will grow from 1.38 billion US dollars to 2.4 billion US dollars, during which the compound annual growth rate will reach 15.5%.
So, what impact does ADAS have on the automotive industry supply chain? In fact, most original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have already planned a blueprint for the development of fully automated driving technology. These OEMs have defined a range of applications and are planning to roll out to end-users between now and 2025, with consequent improvements in ADAS features and functionality during this period.
For ADAS, it is not easy to analyze whether a component is suitable or not, because it requires a combination of various computing power, power consumption, and functional safety requirements. However, most consumer electronic grade semiconductor component products cannot meet such high requirements. Requirements. Safety-focused driver assistance systems that support pedestrian detection/avoidance, lane departure warning/correction, traffic sign recognition, panoramic imaging, fatigue monitoring, etc. These applications, as well as many other applications, require a new class of system Chips to meet the growing needs of the system.
What is an ADAS system?
ADAS is the advanced driving assistance system, also known as the active safety system, which mainly includes the body electronic stability system ESC, adaptive cruise system ACC, lane departure warning system LDW, lane keeping system LKA, forward collision warning system FCW, automatic emergency braking system AEB. Traffic sign recognition TSR, blind spot detection BSD, night vision system NV, automatic parking system APS, etc.
When each type of subsystem in ADAS is in operation, it does not deviate from the collection, processing and judgment of information, and after the judgment is completed, the system gives the body body instructions to make the car perform various stages. In such a process, sensors such as radars and cameras, as well as processors such as MCUs or image processing ICs, have become the most important components.
Not only that, but the ADAS subsystem can use more than one sensing method. Taking the parking assist system as an example, when the driver performs the "parking" action, the rear side image displayed on the screen of the car and the radar warning sound when the vehicle body is too close to the obstacle are the simultaneous use of the image. And the results of radar sensing.
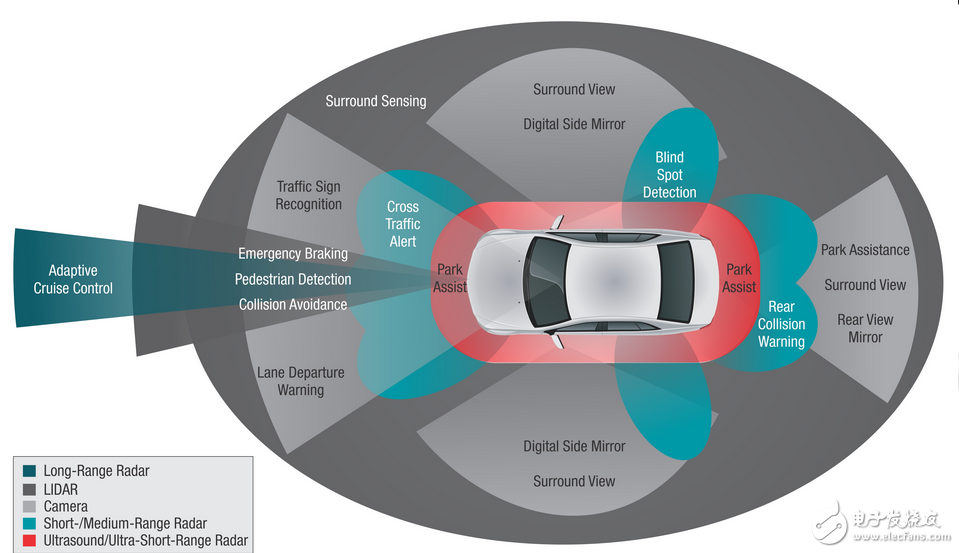
It is worth mentioning that not all subsystems of ADAS have independent sensors. Sometimes different systems can share the same camera. For example, the rear lens that is placed in the center of the car can capture the front lens of the image in front of the car body. In the front collision warning and lane offset warning system, the back end processor can perform the calculation separately.
Vehicle radars include ultrasonic radar, millimeter wave radar and light wave radar, each with its own advantages. The mainstream radars most commonly used in ADAS systems are millimeter-wave radars, including short/medium range radars with a frequency range of 24 GHz (detection distances of about 50 to 70 meters) and long-range radars of 77 GHz. In recent years, the radar in the 79 GHz band has begun to attract attention. Its accuracy is 2 to 4 times that of the 77 GHz radar, and the detection distance is about 70 meters. It belongs to the middle distance radar category and has the opportunity to replace some of the 24 GHz radar market, but because of the 79 GHz in many The country is a frequency band that has not yet been opened, and the development trend remains to be seen.
Since ADAS systems can use images as one of the modes of assisted driving, image sensors have grown significantly in recent years. If radar and image sensing can match each other, they will achieve complementary effects. Therefore, adding a sensing fusion technology that integrates different signals into the processor or MCU allows the processor to calculate multiple signals, which becomes an important trend. However, when developing this technology, it is also necessary to consider the time delay of the image signal and the radar signal together in the calculation process.
KNM3 Series Moulded Case Circuit Breaker
KNM3 series Moulded Case Circuit Breaker is MCCB , How to select good Molded Case Circuit Breaker suppliers? Korlen electric is your first choice. All moulded Case Circuit Breakers pass the CE.CB.SEMKO.SIRIM etc. Certificates.
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker /MCCB can be used to distribute electric power and protect power equipment against overload and short-current, and can change the circuit and start motor infrequently. The application of Moulded Case Circuit Breaker /MCCB is industrial.
Korlen electric also provide Miniature Circuit Breaker /MCB. Residual Current Circuit Breaker /RCCB. RCBO. Led light and so on .
KNM3 series Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Small Size Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Electrical Molded Case Circuit Breaker,Automatic Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Wenzhou Korlen Electric Appliances Co., Ltd. , https://www.zjaccontactor.com