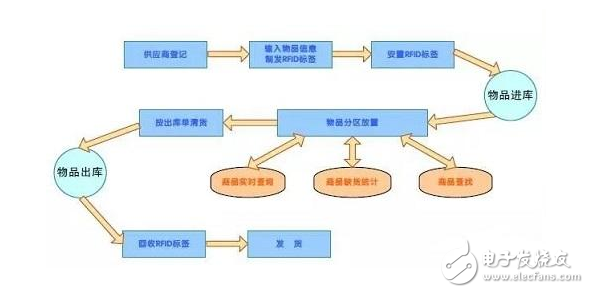
Intelligent logistics is the use of bar code, radio frequency identification technology, sensors, global positioning system and other advanced Internet of Things technology through information processing and network communication technology platform is widely used in the logistics industry transportation, warehousing, distribution, packaging, loading and unloading and other basic activities to achieve goods The automated operation of the transportation process and high-efficiency optimization management improve the service level of the logistics industry, reduce costs, and reduce the consumption of natural resources and social resources. The Internet of Things provides a good platform for the logistics industry to combine traditional logistics technology with intelligent system operation management, so as to realize the informationization, intelligence, automation, transparency and system operation of intelligent logistics better and faster. mode. In the process of implementation, intelligent logistics emphasizes the intelligentization of logistics process data, network synergy and intelligent decision-making. Intelligent logistics must achieve six “correct†functions, namely correct goods, correct quantity, correct location, correct quality, correct time, and correct price. Technically: item identification, location tracking, Item traceability, item monitoring, real-time response.
The main technology of intelligent logisticsAutomatic identification technology
Automatic identification technology is a highly automated data acquisition technology based on the development of computer, optical, mechanical, electrical, and communication technologies. It acquires relevant information of the recognized object by applying a certain identification device, and provides a technology to the background processing system to complete related subsequent processing. It can help people to quickly and accurately collect and input massive amounts of data, and has been widely used in transportation, warehousing and distribution. After nearly 30 years of development, automatic identification technology has developed into a comprehensive technology consisting of bar code recognition technology, smart card recognition technology, optical character recognition technology, radio frequency identification technology, biometric technology, etc., and is developing towards integrated applications.
Barcode recognition technology is currently the most widely used automatic identification technology. It uses photoelectric scanning equipment to read bar code symbols to realize automatic information entry. A bar code is a symbol that represents a certain amount of information consisting of a set of bars, spaces, and corresponding characters arranged according to a specific rule. Different code systems have different composition rules for bar code symbols. The more commonly used code systems are: EAN/UPC bar code, 128 bar code, ITF - 14 bar code, interlaced two or five bar code, thirty nine bar code, Kudba bar code, etc. Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is a modern automatic identification technology developed in recent years. It is a non-contact reading of radio frequency tags by readers and receivers using induction, radio wave or microwave technology to achieve automatic data collection. . It can recognize high-speed moving objects, and can also read multiple objects at the same time. It has the characteristics of resisting harsh environment and strong confidentiality.
Biometric technology is a technology that uses human physiology or behavioral characteristics for identity identification. Biological features include hand shape, fingerprint, face shape, iris, retina, pulse, auricle, etc. Behavioral characteristics include signature, sound, and the like. Due to the non-replicable nature of human body features, the security of this technology is greatly improved compared to the traditional identity verification mechanism. Six biometric recognition technologies such as iris recognition technology, retina recognition technology, facial recognition technology, signature recognition technology, voice recognition technology and fingerprint recognition technology have been developed.
Data mining technology
The data warehouse appeared in the mid-1980s. It is a topic-oriented, integrated, non-volatile, time-varying data set. The goal of the data warehouse is to process data from different sources with different structures. Storage, extraction and maintenance in the data warehouse, it supports comprehensive, large-scale analysis and processing of complex data and high-level decision support. The data warehouse gives users the freedom to extract data arbitrarily without disturbing the normal operation of the business database. Data mining is the process of mining implicit, unknown, and potentially valuable knowledge and rules from a large number of incomplete, noisy, fuzzy, and random real-world applications. It is generally divided into descriptive data mining and predictive data mining. Descriptive data mining includes data summarization, clustering and association analysis. Predictive data mining includes classification, regression and time series analysis. Its purpose is to reveal the interrelationships between events through the statistics, analysis, synthesis, induction and reasoning of data, to predict future development trends, and to provide decision-making basis for decision makers.
Artificial intelligence technology
Artificial intelligence is a discipline that explores ways to simulate human intelligence through various machines and to materialize and extend human intelligence. It draws on the idea of ​​bionics and abstracts knowledge in mathematical language to imitate the intelligent mechanisms of biological systems and humans. The main methods are neural network, evolutionary computation and granular computing. Neural network: Neural network is a kind of parallel processing network that is based on the research of biological neural network to simulate human image intuition thinking. According to the characteristics of biological neurons and neural networks, it is simplified, summarized and refined.
The main functions of neural networks are associative memory, classification clustering and optimization calculation. Although neural networks have the disadvantages of complex structure, poor interpretability, and long training time, they have the advantages of high tolerance to noise data and low error rate, as well as various network training algorithms such as network pruning algorithm and rule extraction algorithm. Constantly put forward and perfect, making the application of neural network in data mining more and more popular for the majority of users. Evolutionary Computation: Evolutionary computation is a general solution to the problem developed by simulating biological evolution theory. Because it is derived from the biological evolution of nature, it has the strong adaptability characteristics shared by natural organisms, which makes it possible to solve complex problems that are difficult to solve by traditional methods.
It uses a multi-point parallel search method, through evolutionary operations such as selection, crossover and mutation, repeated iterations, and under the guidance of individual fitness values, the results of each generation of evolution are better than the previous generation, so evolved from generation to generation. Until a global optimal solution or a global near optimal solution is generated. The most representative one is the genetic algorithm, which is an adaptive optimization algorithm based on the biological genetic evolution mechanism of nature. Granular calculation: As early as 1990, famous Chinese scholars Zhang Wei and Zhang Ling discussed the issue of granularity and pointed out that "a recognized feature of human intelligence is that people can get from very different granularity (granulari2ty). Observing and analyzing the same problem. People can not only solve problems in a world of different granularity, but also quickly jump from one granular world to another, and have no difficulty.
This ability to deal with different granular worlds is a powerful manifestation of human problem solving.†Later, when Zadeh discussed fuzzy information granularity theory, he proposed three main concepts of human cognition, namely granularity (including the decomposition of the whole into parts). ), organization (including partial integration of all) and causal (including causal associations), and further proposed granular computing. He believes that granular computing is a big umbrella, covering all the theory, methodology, technology and Research on tools. At present, there are three kinds of fuzzy set theory, rough set theory and quotient space theory.
GIS technology
GIS is the key technology and tool for building intelligent logistics. Using GIS, you can construct a map of logistics, and manage the order information, network information, delivery information, vehicle information, customer information and other data in one picture to achieve fast and intelligent ordering. Reasonable layout of outlets, reasonable planning of delivery routes, package monitoring and management.
GIS technology can help logistics companies implement map-based services, such as:
1. Marking of outlets: Label the outlets and outlets of logistics enterprises (such as address, telephone, delivery and other information) on the map, which is convenient for users and enterprise managers to quickly query.
2. Area division: Manage big data from the perspective of “geographic spaceâ€, provide basic services for business division management for logistics business systems, such as dividing logistics responsibility areas, etc., and associate with outlets.
3, fast split: use GIS address matching technology, search for location zoning units, and quickly assign addresses to regions and outlets. According to the attributes of the logistics division unit, the responsible person is found to realize the “last mile†delivery.
4, vehicle monitoring and management system, from the goods out of the warehouse to reach the customer's hands to monitor the entire process, reduce the loss of goods; rationally dispatch vehicles, improve vehicle utilization; various alarm settings to ensure the safety of cargo drivers and save enterprise resources.
5. The logistics distribution route planning auxiliary system is used to assist the logistics distribution planning. Reasonably plan the route to ensure the fast arrival of goods, save enterprise resources and improve user satisfaction.
6. Data statistics and services, visualize and visualize the data information of logistics enterprises on the map, and use scientific business models, GIS professional algorithms and spatial mining analysis to gain insight into the trends and internal relationships that cannot be understood through other means, thus Various business activities, such as developing marketing strategies, planning logistics routes, rational site selection analysis, analysis and forecasting development trends, etc., build a good foundation to make business decision systems more intelligent and accurate, thus helping logistics companies to obtain greater market opportunities.
Key technologies of intelligent logistics1, loading technology (loading, route optimization)
The loading technology is the key technology for integrating time, cost, resources, efficiency and environmental constraints under the premise of accomplishing one or more operational objectives, realizing the low cost and high efficiency of modern logistics management, and is the logistics operation plan and actual operation. The key to effective binding between.
2, the distribution line optimization technology
Optimization of the collection line, cargo assembly and delivery line optimization are the key to the optimization of the distribution system.
3, loading and unloading technology
Traditionally, loading and unloading technology refers to activities carried out in the same geographical area with the main content and purpose of changing the storage state and spatial position of the object, specifically including loading, unloading, transferring, selecting, sorting, and stacking. Activities such as squatting, warehousing, and warehousing.
4, packaging technology
Packaging technology includes packaging technology, packaging materials, packaging design, packaging testing, packaging testing, etc. The use of packaging technology in logistics has a close correlation with packaging technology, packaging materials, packaging design.
5, MilkRun operating technology
MILKRUN cycle picking is carried out by one (or several) transportation contractors according to the pre-designed pick-up route, in order to suppliers A, B, C to pick up the goods, and then directly to the factory or parts redistribution center.
6, process control technology
Modern logistics has become a trend of integration of business flow and information flow. By constructing a modern logistics system and a new modern logistics system, information flow, logistics and information flow are realized with the support of logistics information systems. This will provide accurate and timely logistics services. The development of modern logistics is characterized by the widespread application of information technology.
7, barcode and automatic identification technology
A barcode is a set of strips and spaces that are arranged according to certain encoding rules to represent certain characters, numbers, and symbols. The bar code system is an automatic identification system consisting of bar code symbol design, production and scanning reading.
8, logistics automation technology
Logistics operation automation is an important way and means to improve logistics efficiency, and it is also an important trend in the development of logistics industry.
9, POS system and logistics EDI technology
POS (PointOfSale) system is the point-in-time information system, that is, the sales of dynamic data should be timely transmitted to the production, procurement, and supply links. The POS machine automatically reads the data through the cash register to realize the sharing of real-time data throughout the supply chain. The work efficiency of the station can be greatly improved, and the customer satisfaction is also improved.
10, GIS technology, GPS technology
GIS Geographic Information System is based on geospatial database. With the support of computer hardware and software, it uses the theory of system engineering and information science to scientifically manage and comprehensively analyze geographic data with spatial connotation to provide information needed for management and decision-making. Technical system. Simply put, GIS is a technical system that comprehensively processes and analyzes geospatial data.
SMC Board To Board Connector Section.
Compact high density design
Design of super reliable double beam contact
High speed signal transmission rate up to 3 Gbit / S
Polarization to ensure accurate connection
Locating pin for PCB placement
Welded bracket for secure PCB
Wide operating temperature range
Height range of non matching stack
For full automation board components
SMC Board To Board Connector Section
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkwire.com