The basis for audio signal compression is audio compression technology.
Audio compression technology refers to the use of appropriate digital signal processing technology on the original digital audio signal stream (PCM encoding) to reduce (compress) its code rate without loss of useful information or negligible loss introduced. This is called compression coding. It must have a corresponding inverse transform, called decompression or decoding. The audio signal may introduce a lot of noise and certain distortion after passing through a codec system.
In the field of audio compression, there are two compression methods, namely lossy compression and lossless compression. Common MP3, WMA, OGG are called lossy compression, as the name implies is to reduce the audio sampling frequency and bit rate, the output audio file will be smaller than the original file. Another type of audio compression is called lossless compression, which is the subject matter to be said. Lossless compression can reduce the volume of the audio file on the premise of saving 100% of all data in the original file, and restore the compressed audio file to achieve the same size and the same bit rate as the source file. Lossless compression formats are APE, FLAC, WavPack, LPAC, WMALossless, AppleLossless, La, OpTImFROG, Shorten, and the only common and lossless compression formats are APE and FLAC.
Audio compression technology standards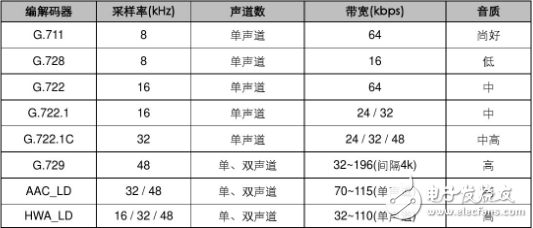
Audio signals are an important part of multimedia information. Audio signals can be divided into telephone-quality language, amplitude-modulated broadcast-quality audio signals, and high-fidelity stereo signals (such as FM broadcast signals, laser disc audio disk signals, etc.). Digital audio compression technology standards are divided into telephone voice compression, AM broadcast voice compression and There are three types of broadband audio compression for FM broadcasting and CD quality.
In the field of voice coding technology, various manufacturers are vigorously developing and promoting their own coding technology, which makes the coding technology products in the field of voice coding have a wide variety of products and poor compatibility. It is difficult for the technologies of various manufacturers to be promoted as soon as possible. Therefore, it is necessary to synthesize the existing coding technology and formulate a globally unified language coding standard. Since the 1970s, the fifteenth study group under ccett and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have successively launched a series of speech coding technology standards. Among them, ccitt launched the g series standard, and iso launched the h series standard.
1. Telephone (200hz-3.4khz) voice compression standards mainly include itu g.722 (64kb / s), g721 (32kb / s), g.728 (16kb / s) and g.729 (8kb / s), etc. Recommended for digital telephone communications.
2. The AM broadcasting (50hz-7khz) voice compression standard mainly uses itu's g.722 (64kb / s) recommendation for high-quality voice, music, audio conferences, and video conferences.
3. Broadband audio compression standards for FM broadcasting (20hz-15khz) and cd sound quality (20hz-20khz) mainly adopt mpeg-1 or mpeg-2 dual Dolby ac-3 and other recommendations, used for cd, md, mpc, vcd, dvd, hdtv and movie dubbing, etc.
The following mainly introduces g.722 (64kb / s) and mpeg-4
G722 audio compression coding standard
G.722 is a multi-frequency speech coding algorithm that supports bit rates of 64, 56 and 48kbps. In G.722, the sampling rate of speech signals is 16000 samples per second. Compared with the 3.6kHz frequency speech coding, G.722 can handle a wide band of audio signals up to 7kHz. The G.722 encoder is based on the principle of subband adaptive differential pulse coding (SB-ADPCM). The signal is divided into two subbands, and ADPCM technology is used to encode the samples of the two subbands.
G.722 is a wideband coding method in the G series of voice coding. Compared with G.711, the sampling frequency is expanded from 8KHZ to 16KHZ. The voice quality is improved. The signal is divided into 2 subbands (high frequency, low frequency). The signal in each subband is encoded using ADPCM (adapTIve differenTIal pulse code modulaTIon). The principle of ADPCM is Only the segment of the incremental change in the sound sample is sampled. In the calculation of the final bit rate, the low frequency part is allocated to more resources 8Kbps X 6bit, and the high frequency part is allocated to less resources (mostly friction sound, noise, etc.) Auxiliary tone) 8Kbps X 2bit, the sum of the two is 64Kbps, so the bit rate of G.722 is 64kbps relative to G.711, but the voice quality is improved. G.722 encoding has been supported in cisco CM7.0 and above The algorithm, cisco 79 and above series switches have adopted G.722 encoding as the default preferred encoding.
MPEG-4 audio compression coding standard
Has a high degree of flexibility and scalability. Mainly serves multimedia communications at low bit rates. Introduction of audio objects (A â—‹)
Code rate range: 2 ~ 64kb / s, provide three types of encoders â‘ Low bit rate: parameterized encoder
Parameter encoder: Use parameter encoding technology.
Two coding tools: harmonic vector excitation coding, harmonic and characteristic line plus noise coding.
â‘¡Intermediate bit rate: code excited linear predictive encoder
Code excited linear predictive encoder: mainly composed of excitation source and synthesis filter
   ③High bit rate: time / frequency encoder
Time / frequency encoder: Time domain module extracts gain information of audio signal
The filter bank transforms the time domain to the frequency domain through the DCT transform signal
Psychoacoustic models adopt corresponding processing strategies for frequency domain signals in different frequency bands
The frequency domain processing module processes signals in various frequency bands according to the parameters of the psychoacoustic module.
The quantization and coding part encodes the frequency domain signal.
Industrial Main Board Cable:SCSI,D-SUB,DVI,Wire to Wire ,RJ45...
There are five types of main board power line interface, and different external devices correspond to different interfaces. Different interfaces and their connecting pins are also different. For example, the pin of the main power supply is 24 pins, and the hard disk drive is 5 pins.
1. 20pin + 4Pin interface: it is a common interface combination, in which 20pin is the main power interface and 4Pin is the auxiliary power supply interface.
2. 5pinsata interface: special interface for power supply of hard disk and optical drive.
3. 6pin? PCI? Express connector: a special interface for independent graphics power supply.
4. 4Pin connector: it is a kind of floppy disk power connector, which is used to power the floppy drive equipment.
5. 4Pin power interface: optical drive, old IDE hard disk and peripheral hardware power supply interface.
Industrial Main Board Cable
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenksocket.com