Cellular network or mobile network (Cellular network) is a mobile communication hardware architecture, which divides the service of mobile phone into small hexagonal sub-areas, and each cell has a base station, which forms a structure similar to "cellular". Therefore, this mobile communication method is called a cellular mobile communication method.
Cellular networks can be divided into analog cellular networks and digital cellular networks, which are mainly distinguished from the way information is transmitted.
Cellular network component
The cellular network consists of the following three parts: mobile station, base station subsystem, and network subsystem. A mobile station is a network terminal device, such as a mobile phone or some cellular industrial control device. The base station subsystem includes a mobile base station (large tower), a wireless transceiver device, a private network (generally a fiber optic), a wireless digital device, and the like. The base station subsystem can be seen as a converter between the wireless network and the wired network.
Cellular and frequency reuse
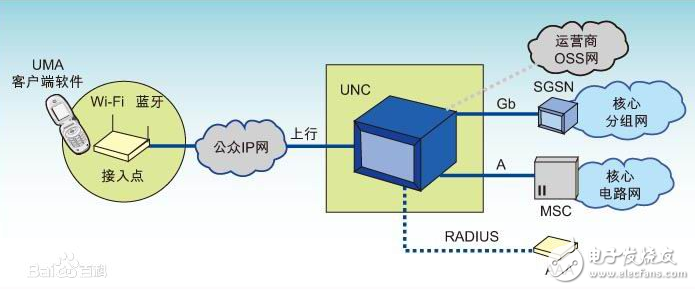
Cellular network
Cellular: A large area is divided into multiple small cells, using multiple low power transmitters instead of one high power transmitter. A regular hexagon is generally used to describe the shape of the honeycomb.
Frequency reuse: Each cell uses a set of channels. If the two cells are far enough apart, the same set of channels can be used. Cluster: A group of cells consisting of N cells, using all frequency resource frequency reuse factors (reusefactor): 1/N for regular hexagonal cells, N=i^2+i*j+j^ 2, i "=1, j" = 1, when i "1, j ≥ 0 or when j "1, i ≥ 0. Therefore, N = 3, 4, 7, 9, 12. .
Geometric representation of the honeycomb
Honeycombs are usually represented by regular hexagons. Why is a regular hexagon instead of a circle? From the vertices to the equidistant polygons in the geometric center, the possible geometric shapes of a region can be covered completely (without overlapping): square, equilateral triangle and regular hexagon. In squares, equilateral triangles, and regular hexagons, the area of ​​the regular hexagon is the largest.
Cellular coordinate system
Use (i, j) to represent the coordinates of a certain cell. For example: the coordinates of cell A are (2, 1)
Cellular channel allocation
FDMA system: Using the principle of signal attenuation. Key: Divide the spectrum into channels (user channel carriers) that can be multiplexed when the distance is far enough.
Static channel allocation: Each cell is pre-allocated with a fixed set of channels, which is simple to implement.
Dynamic channel allocation: The base station dynamically allocates a channel from the MSC. The cell can use all channels, which reduces the blocking probability and is complex. It requires real-time traffic detection and coordinated processing between base stations.
Cellular network service functionMobile Station (MS): A mobile communication device, such as a mobile phone or a mobile station, may also be equipped with a terminal device or a terminal adapter.
Base Transceiver Station (BTS): Includes all kinds of hardware and software required for wireless transmission. Such as the antenna, the interface circuit connecting the base station controller, and the detection and control devices required by itself.
Base Station Controller (BSC): Provides an interface for exchanging information between the BTS and the MSC and between the BTS and the OMC. The main functions are to perform wireless channel management, implement the establishment and removal of call and communication links, and control the handover of mobile stations in the control area.
Mobile Switching Center (MSC): The core of a cellular communication network. The main function is to control and manage the mobile users located in the control area of ​​the MSC.
Home Location Register (HLR): A database used to store local user location information. Visit Location Register (VLR): is a database used to store visitor location information.
Authentication Center (AUC): Its role is to reliably identify the user's identity, allowing only authorized users to access the network and obtain services.
Device Flag Register (EIR): A database that stores mobile device parameters. Used for authentication and monitoring of mobile devices and denying illegal mobile stations access to the network.
Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC): The task is to monitor and operate the entire network.
Dash Mining Machine:Bitmain Antminer D7 (1286Gh),Baikal BK-G28,Baikal BK-X,Baikal Giant+ A2000,Innosilicon A5 DashMaster,iBeLink DM22G,Bitmain Antminer D3 (15Gh),StrongU STU-U6,Bitmain Antminer D5 (119Gh)
In short, Dashcoin Dash is a variant of the Bitcoin cryptocurrency that runs on the same blockchain network. Dashi, which combines the words "digital" and "cash," has become one of the most widely watched counterfeit coins in recent months. Originally released as "XCoin", it was later changed to "Darkcoin" and later Dash.
Arguably the biggest benefit of Dashi is that its transactions can be sent completely anonymously, just like legal cash payments. This is achieved by using a hybrid protocol that operates a dedicated network of servers called Masternodes. While Bitcoin operates only a single-layer network of miners, Dashcoin uses these master nodes as additional layers to its network, eliminating the need for a trusted third party to authorise a transaction that could compromise the anonymity of any payment.
Another major difference between Dashcoin and Bitcoin is that the former distributes mining rewards between its mining community, participants holding a specified amount of Dash, and the Dash community's long-term development fund.
Dash Miner,Dash Mining Machine,Bitmain antminer d7, D7 miner,X11 algorithm
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.asicminer-ylhm.com